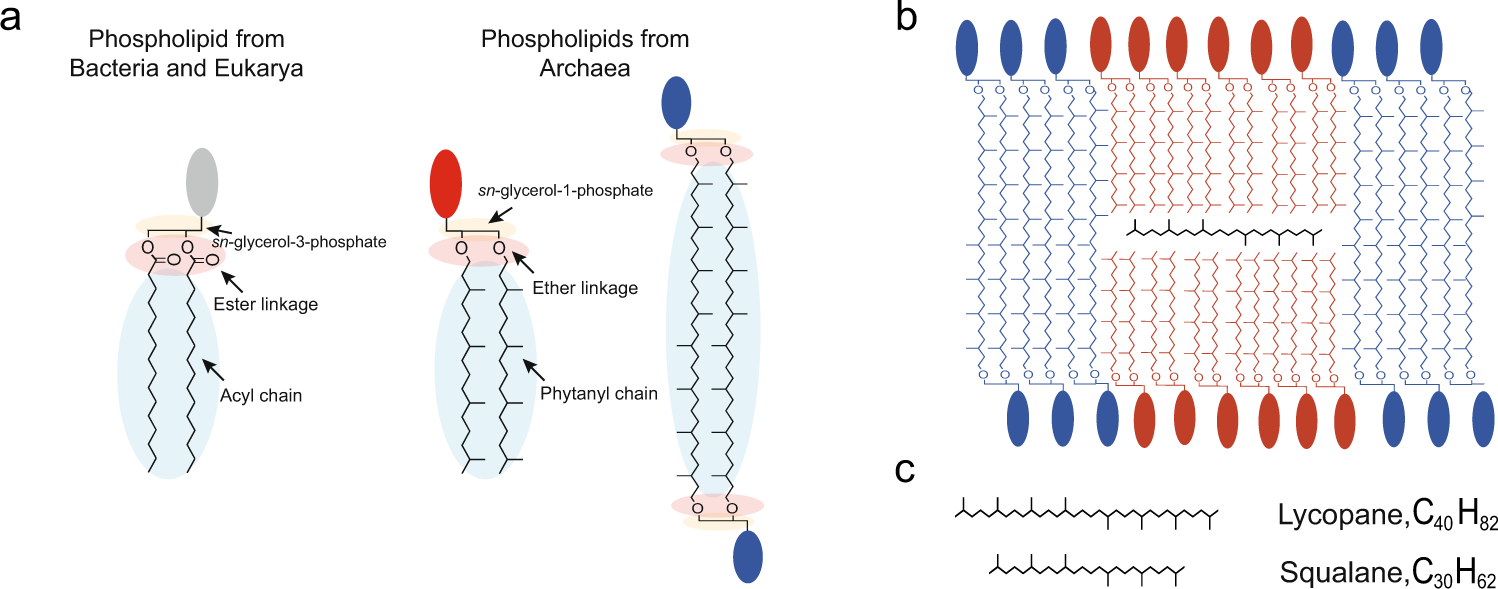
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell and serves as a protective layer, separating the internal environment of the cell from the external environment. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and function of the cell, and it is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which is a double layer of phospholipid molecules arranged in such a way that the hydrophilic (water-loving) heads face outward, while the hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails face inward. The structure of the phospholipid bilayer is dynamic, and the movement of phospholipid molecules within the membrane is essential for the proper functioning of the cell.
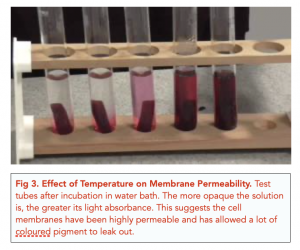
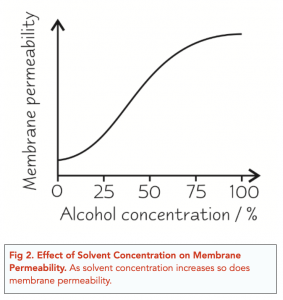
One of the factors that can affect the structure and function of the cell membrane is temperature. The temperature of the environment in which a cell lives can have a significant impact on the fluidity of the cell membrane, which in turn can affect the movement of substances across the membrane.
At low temperatures, the phospholipid molecules in the cell membrane become more rigid and less fluid, which can affect the movement of substances across the membrane. At these temperatures, the movement of ions and small molecules such as oxygen and glucose may be slowed down or even stopped, disrupting the normal functioning of the cell. In addition, the low temperature can cause the cell membrane to become more permeable, allowing more substances to pass through the membrane and potentially damaging the cell.
On the other hand, at high temperatures, the phospholipid molecules in the cell membrane become more fluid and flexible, which can also affect the movement of substances across the membrane. At these temperatures, the movement of ions and small molecules may be increased, leading to an increased metabolism and potentially damaging the cell. In addition, the high temperature can cause the cell membrane to become less permeable, which may hinder the movement of necessary substances into the cell and disrupt the normal functioning of the cell.
In conclusion, the temperature of the environment can have a significant effect on the structure and function of the cell membrane. At low temperatures, the cell membrane becomes more rigid and permeable, while at high temperatures, it becomes more fluid and less permeable. Both of these conditions can disrupt the normal functioning of the cell and potentially damage it. Therefore, it is important for cells to maintain a constant temperature within a narrow range in order to maintain the proper functioning of the cell membrane and the overall health of the cell.