Eugen goldstein contribution. Eugene Goldstein (1885) 2022-12-31
Eugen goldstein contribution
Rating:
8,1/10
1121
reviews
Eugen Goldstein was a German physicist who made significant contributions to the field of electrical discharge in gases, or plasma physics. He is known for his discovery of anode rays, which are streams of positive ions that are emitted from the anode of a discharge tube. This discovery laid the foundation for the study of plasma, which is a state of matter in which electrons are separated from the atomic nucleus, resulting in a highly ionized gas.
Goldstein's work on anode rays was significant because it challenged the prevailing theory of the time, which stated that electricity flowed only through metal conductors. His experiments showed that electricity could also flow through gases, and this finding opened up a whole new field of study in physics.
In addition to his work on anode rays, Goldstein also made important contributions to the study of cathode rays, which are streams of negative particles that are emitted from the cathode of a discharge tube. He discovered that cathode rays were deflected by magnetic fields, which led to the development of the cathode ray tube (CRT), a device that is used in televisions and computer monitors to display images.
Goldstein's contributions to the study of electrical discharge in gases had a significant impact on the development of modern technologies such as plasma televisions and neon lights. His work also laid the foundation for the study of nuclear fusion, which is a process that releases energy by combining atomic nuclei.
In conclusion, Eugen Goldstein made significant contributions to the field of plasma physics through his discovery of anode rays and his work on cathode rays. His findings had a lasting impact on the development of modern technologies and the understanding of the nature of matter.
What was Eugen Goldstein contribution to the atomic theory?

Eugen Goldstein He was a leading German physicist, born in modern Poland in 1850. With this conclusion, the fact that the particles came out of the interior of the gas, and not of the anode of the electrified tube, was clarified. The Raisin Pudding Model of the Atom Eugen Goldstein Goldstein concluded that in addition to the electrons, or cathode rays, that travel from the negatively charged cathode toward the positively charged anode, there is another ray that travels in the opposite direction, from the anode toward the cathode. What did Eugen Goldstein discover about the cathode ray? Consequently, the relationship between the electrical charge and the mass of the particles will be different depending on the nature of the gas that is being used during the experiment. One of his most outstanding legacies consisted in the discovery of what today are known as protons, together with channel rays, also known as anodic or positive rays.
Next
Goldstein
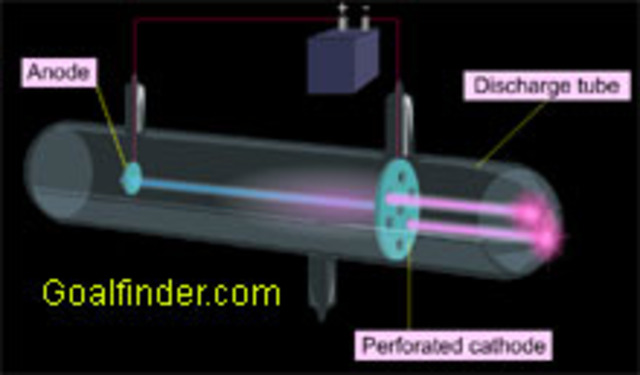
His scientific work includes experiments with electrical phenomena in gases and cathode rays. Goldstein identified the existence of protons as equal and opposite charges to electrons. The discovery of the proton, as counterpart of the electron, laid the foundations for the construction of the atomic model that we know today. Nevertheless, Ernest Rutherford is considered the discoverer in the scientific community. La découverte du proton, en contrepartie de l'électron, a jeté les bases de la construction du modèle atomique que nous connaissons aujourd'hui. However, it was left to one of his students to discover that these rays were sometimes pure protons. The positively charged ions that make up the channel rays move towards the perforated cathode until they pass through it, given the nature of the experiment.
Next
What did Eugen Goldstein experiment?

Modification of cathode tubes Likewise, Eugen Godlstein's essays also contributed significantly to deepening technical notions about cathode rays. Goldstein did not propose an atomic model, although his discoveries allowed the development of the atomic model of Thomson. How did Goldstein prove the existence of protons in an atom? Goldstein observed rays travelling in the opposite direction of the cathode rays in a cathode ray tube. Cependant, le fait saillant est que ces rayons se sont déplacés dans la direction opposée aux rayons de la cathode et ont été appelés rayons de canaux. He is credited with the discovery of protons. On the other hand, he is sometimes credited as the discoverer of the proton, which he observed in the vacuum tubes where he observed cathode rays.
Next
What was the contribution of Goldstein in chemistry?
Which is correct statement about Proton? How did Eugen Goldstein contribute to the field of Science? In 1895, Wilhelm Roentgen, experimenting with cathode rays, discovered new and different kinds of rays. His scientific work includes experiments with electrical phenomena in gases and cathode rays. This new flow was baptized by Goldstein as channel rays. What role did Eugen Goldstein play in determining the subatomic particles and in what year? Channel rays, also known as anodic rays or positive rays, depend directly on the physical-chemical characteristics of the gas that is contained within the tube. Who was Eugen Goldstein and what did he do? Through experiments on evacuated tubes, Goldstein detected that cathode rays could project acute shadows of emission perpendicular to the area covered by the cathode. La structure de base du tube de Crookes consiste en un tube vide en verre dans lequel circulent des gaz. If possible, verify the text with references provided in the foreign-language article.
Next
How did Eugen Goldstein contribute to the atomic theory?

He found that the atom consists mostly of empty space, with its mass concentrated in a central positively charged nucleus. Those were the Canal rays. Eugen Goldstein was a prominent German physicist, born in present-day Poland in 1850. Cathode ray experiments Crookes tubes Goldstein began his experiments with Crookes tubes in the 1970s. He noticed that a second stream of particles was attracted to the negatively-charged electrode the anode , so he called them anode rays.
Next
Eugen Goldstein

This new flow was baptized by Goldstein as channel rays. Classification Baryon Discovered Observed as H+ by Eugen Goldstein 1886. D'autre part, les rayons des canaux, également appelés rayons anodiques ou rayons positifs, dépendent directement des caractéristiques physico-chimiques du gaz contenu dans le tube. Using a cathode ray tube with holes in the cathode, he noticed that there were rays traveling in the opposite direction from the cathode rays. Who did Eugen Goldstein work with? He was primarily interested in electrical discharges in moderate to high vacuums. This type of notion was key in what is now known as atomic physics, that is, the field of physics that studies the behavior and properties of atoms in their entirety.
Next
Eugen Goldstein: Discoveries and Contributions

Is there an atomic model of Eugen Goldstein? Canal Ray experiment is the experiment performed by German scientist Eugen Goldsteinin 1886 that led to the discovery of the proton. Under this new configuration, Goldstein discovered that the tube emitted a new glow from the end of the tube that had been pierced. What is Goldstein experiment? Eugen Goldstein, born Sept. Isotope study Thus, Goldstein's analysis led to the study of isotopes, for example, among many other scientific applications that are currently in full force. Cette découverte a été réalisée par expérimentation avec des tubes cathodiques, en 1886. Eugene Goldstein 1850-1930 was a German Physicist that discovered that protons have an equal and opposite charge as an electron.
Next
Eugen Goldstein Découvertes et Contributions

Who actually discovered proton? This discovery was very useful to modify the design of the cathode tubes used to date, and to place concave cathodes in their corners, to produce focused rays that would be used in a variety of applications in the future. Using a cathode ray tube with holes in the cathode, he noticed that there were rays traveling in the opposite direction from the cathode rays. La havane, cuba Récupéré de: ecured. En outre, il a répété l'expérience avec la modification du tube de Crookes, en augmentant la tension entre les extrémités du tube à plusieurs milliers de volts. Goldstein a appelé ces rayons "Kanalstrahlen", pour faire référence à la contrepartie des rayons cathodiques. The color assignment of individual quarks is arbitrary, but all three colors must be present. The gas atoms lose their negative charge, and become positively charged.
Next
What is Eugene Goldstein contribution to the atomic theory?
Gas atoms lose their negative charge, and are positively charged. However, Ernest Rutherford is considered the discoverer in the scientific community. He assumed that these new rays had equal and opposite charge of the electron. When Goldstein sent the Cathode rays through the Cathode ray, which are full of electrons, he observed that there were rays going in the opposite direction. An object, such as a small ball of glass or iron, placed in the path of cathode rays produces secondary emissions to the sides, flaring outwards in a manner reminiscent of a comet's tail. Proton The quark content of a proton. In addition, he repeated the experiment with the modification of the Crookes tube, increasing the voltage between the ends of the tube to several thousand volts.
Next






