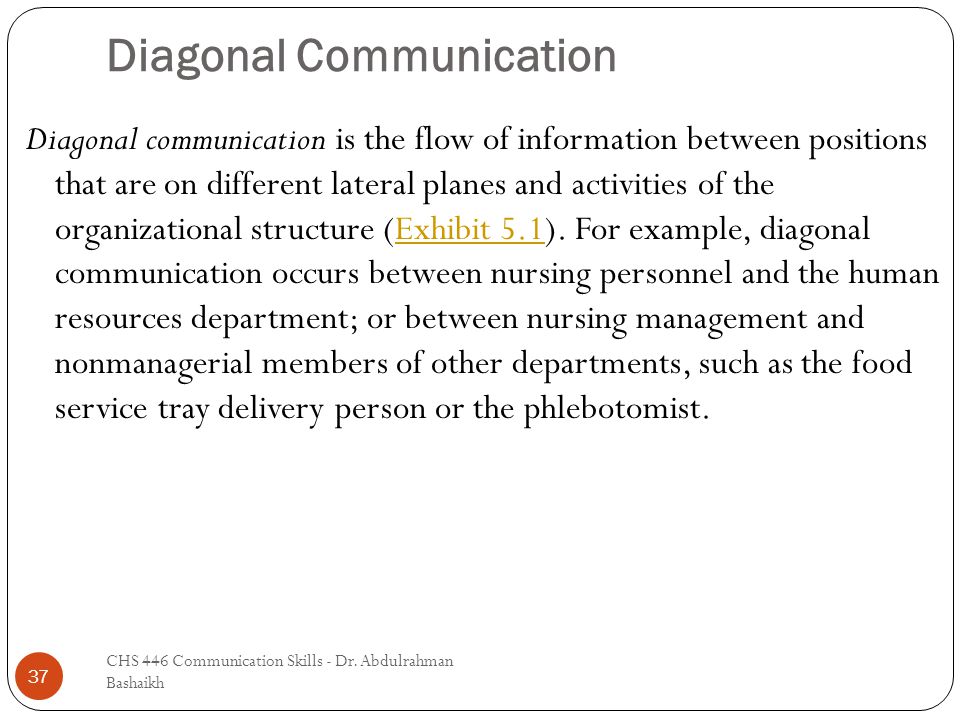
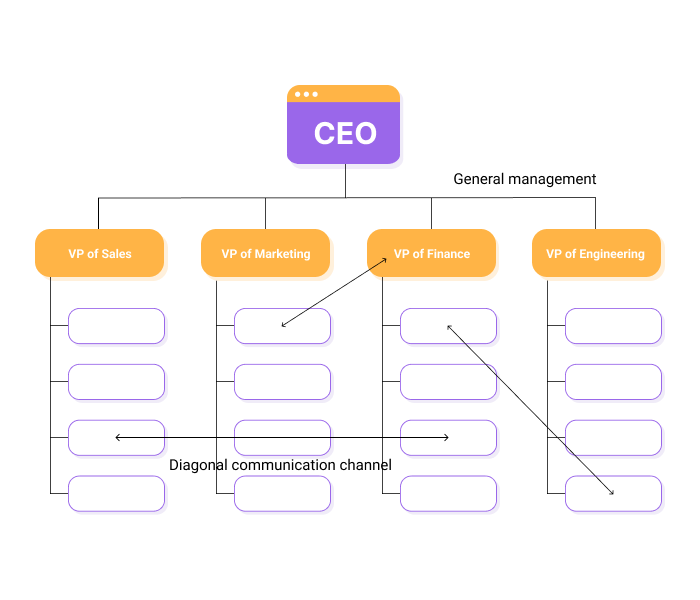
Diagonal communication, also known as cross-functional communication, is the exchange of information and ideas between individuals or teams that operate in different departments, functions, or levels within an organization. This type of communication is important because it helps to break down silos, foster collaboration, and facilitate the flow of information and knowledge across the organization.
One example of diagonal communication is when a marketing team works with a product development team to co-create a new product. The marketing team may provide insights on customer needs and preferences, while the product development team brings technical expertise to the table. Through open communication and collaboration, the two teams can identify and address potential roadblocks, come up with creative solutions, and ultimately launch a successful product.
Another example of diagonal communication is when a manager communicates with employees from different departments to gather feedback and ideas for improving processes and increasing efficiency. By soliciting input from a diverse group of individuals, the manager can gain a more well-rounded perspective and identify opportunities for improvement that may have been overlooked.
Diagonal communication is also important when it comes to decision-making. For example, a human resources team may work with a finance team to determine the best way to allocate resources for employee training and development. By collaborating and sharing information, the two teams can make informed decisions that align with the organization's goals and priorities.
In conclusion, diagonal communication plays a crucial role in enabling organizations to work effectively and efficiently. By facilitating the exchange of information and ideas between individuals and teams from different departments, functions, and levels, diagonal communication helps to break down silos, foster collaboration, and improve decision-making.