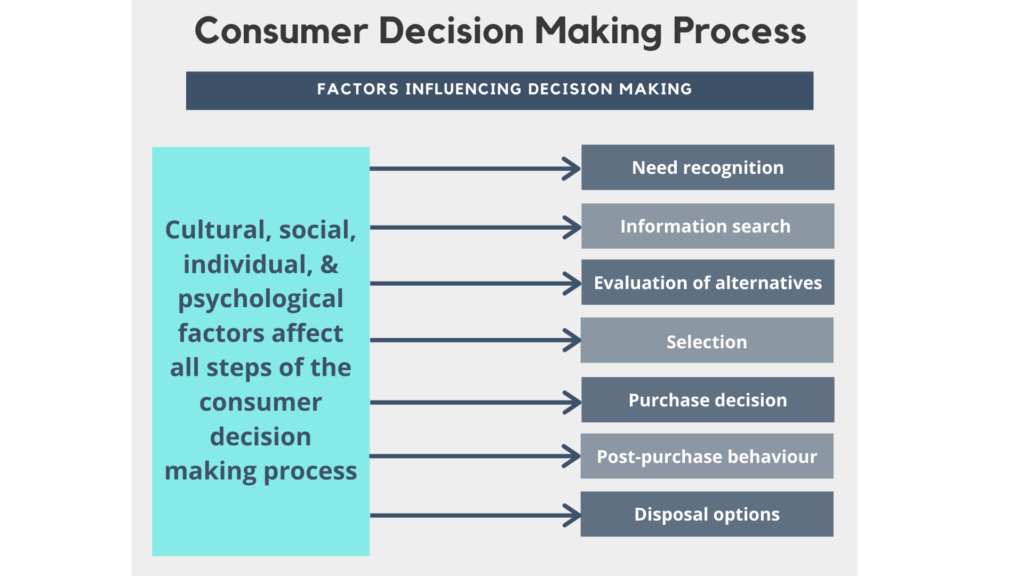
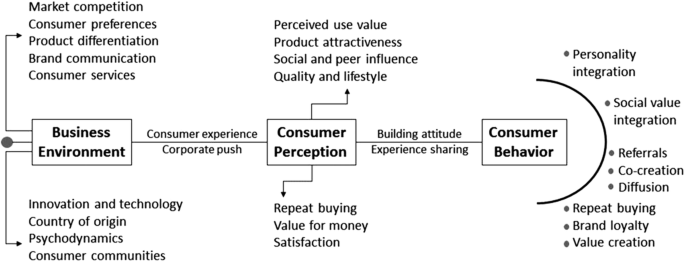
Consumer behavior is influenced by a variety of internal and external factors, including personal, psychological, and social factors. In this essay, we will focus on external influences on consumer behavior, which refer to the external factors that can shape and alter the way consumers make purchasing decisions. These external influences can be grouped into four main categories: cultural, social, personal, and situational.
Cultural influences are perhaps the most fundamental and enduring of all external influences on consumer behavior. Culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, customs, behaviors, and artifacts that characterize a group or society. It is the foundation upon which individuals base their decisions, attitudes, and actions. Culture influences consumer behavior in many ways, including what products and services consumers purchase, how they use them, and how they dispose of them. For example, in some cultures, status and prestige are highly valued, and consumers may be more likely to purchase luxury brands or products that are perceived as high-quality and exclusive. In other cultures, collectivism and community may be more important, and consumers may be more likely to purchase products that reflect these values, such as fair trade or locally-produced products.
Social influences refer to the influence of other people on an individual's behavior. These can include the influence of family, friends, and other reference groups, as well as the influence of the media and society at large. For example, consumers may be influenced by the opinions and recommendations of their friends and family, particularly when it comes to products and services that have a high level of personal or emotional significance, such as clothing, food, or home furnishings. Social media also plays a significant role in shaping consumer behavior, as it allows consumers to connect with others and share their experiences and opinions about products and brands.
Personal influences refer to the individual characteristics and experiences of a consumer that shape their behavior. These can include factors such as age, gender, education, income, occupation, and personality. For example, older consumers may have different purchasing habits and priorities than younger consumers, and consumers with higher incomes may be more likely to purchase luxury or high-end products. Personal experiences and life stages, such as marriage, parenthood, or retirement, can also influence consumer behavior, as consumers may have different needs and priorities at different points in their lives.
Situational influences refer to the immediate circumstances that can affect consumer behavior, such as the physical environment, the time of day, and the consumer's mood or emotional state. For example, consumers may be more likely to make impulsive or spontaneous purchases when they are in a good mood, or when they are in a physical environment that is conducive to shopping, such as a well-designed store or mall. Situational influences can also include external factors such as promotions, sales, or discounts, which can influence consumers to purchase products or services that they might not have otherwise considered.
In conclusion, external influences on consumer behavior are numerous and varied, and they can have a significant impact on the way consumers make purchasing decisions. Understanding these influences can be valuable for businesses and marketers as they develop marketing strategies and target specific consumer segments. By considering the cultural, social, personal, and situational factors that influence consumer behavior, businesses can create more effective and targeted marketing campaigns and better meet the needs and preferences of their customers.