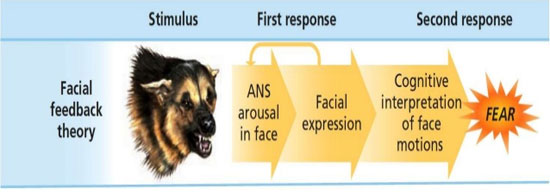
Facial feedback theory is a psychological concept that suggests that the facial expressions we make can influence our emotional state. This theory was first proposed by Charles Darwin in the 19th century, and it has since been supported by a large body of research.
According to facial feedback theory, when we make facial expressions that are associated with a particular emotion, such as smiling when we are happy or frowning when we are angry, we can actually increase or decrease the intensity of that emotion. For example, if you smile when you are feeling down, you may find that your mood improves as a result of the smile. On the other hand, if you frown when you are feeling happy, you may find that your mood becomes more negative.
There are several ways in which facial feedback theory might work. One possibility is that the muscles in our face send signals to the brain that help to regulate our emotional state. For example, when we smile, the muscles in our face send signals to the brain that may help to increase the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which can help to improve our mood. Similarly, when we frown, the muscles in our face may send signals to the brain that may decrease the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which can lead to a negative mood.
Another possibility is that our facial expressions influence the way that we interpret the events around us. For example, if we are feeling happy and we smile, we may be more likely to interpret events in a positive way. On the other hand, if we are feeling down and we frown, we may be more likely to interpret events in a negative way. This suggests that our facial expressions can play a role in shaping our emotional experiences.
There is also some evidence to suggest that facial feedback theory may have an impact on our social interactions. For example, if we are smiling and making positive facial expressions when we interact with others, they may be more likely to respond in a positive way. On the other hand, if we are frowning and making negative facial expressions, they may be more likely to respond in a negative way.
Overall, facial feedback theory is a fascinating concept that has the potential to shed light on the complex relationship between our emotions, our facial expressions, and our social interactions. While there is still much research to be done in this area, the evidence so far suggests that our facial expressions can play a significant role in shaping our emotional experiences and the way that we interact with others.