The exchange rate between the United States dollar (USD) and the Indian rupee (INR) is influenced by a variety of factors. These include economic conditions, government policies, and market forces.
One major factor that affects the USD-INR exchange rate is the relative strength of the two economies. When the Indian economy is growing at a faster rate than the US economy, demand for the INR increases, which can cause the exchange rate to appreciate. On the other hand, if the US economy is growing more quickly than the Indian economy, demand for the USD may increase, leading to a depreciation in the exchange rate.
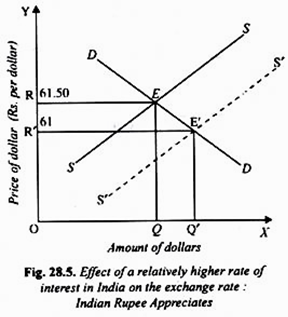
Government policies can also have an impact on the exchange rate. For example, if the Indian government takes steps to stimulate economic growth, such as lowering interest rates or increasing government spending, it can lead to an appreciation in the INR. Conversely, if the US government takes steps to curb inflation, such as raising interest rates, it can lead to a depreciation in the USD.
Market forces, such as supply and demand, also play a role in determining the exchange rate. If there is a large demand for INR, due to increased trade or investment in India, the exchange rate may appreciate. On the other hand, if there is a large supply of INR on the market, due to a decrease in demand or an increase in the money supply, the exchange rate may depreciate.
Other factors that can affect the USD-INR exchange rate include political instability, natural disasters, and global economic trends. For example, if there is political unrest in India or the US, it could lead to a decline in the value of the INR or USD, respectively. Similarly, if there is a natural disaster that affects one of the countries, it could lead to a decline in the value of its currency. Global economic trends, such as changes in the price of oil or other commodities, can also impact the exchange rate between the USD and INR.
In summary, the exchange rate between the USD and INR is influenced by a variety of factors, including economic conditions, government policies, market forces, political instability, natural disasters, and global economic trends. Understanding these factors can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about currency exchange and international trade.