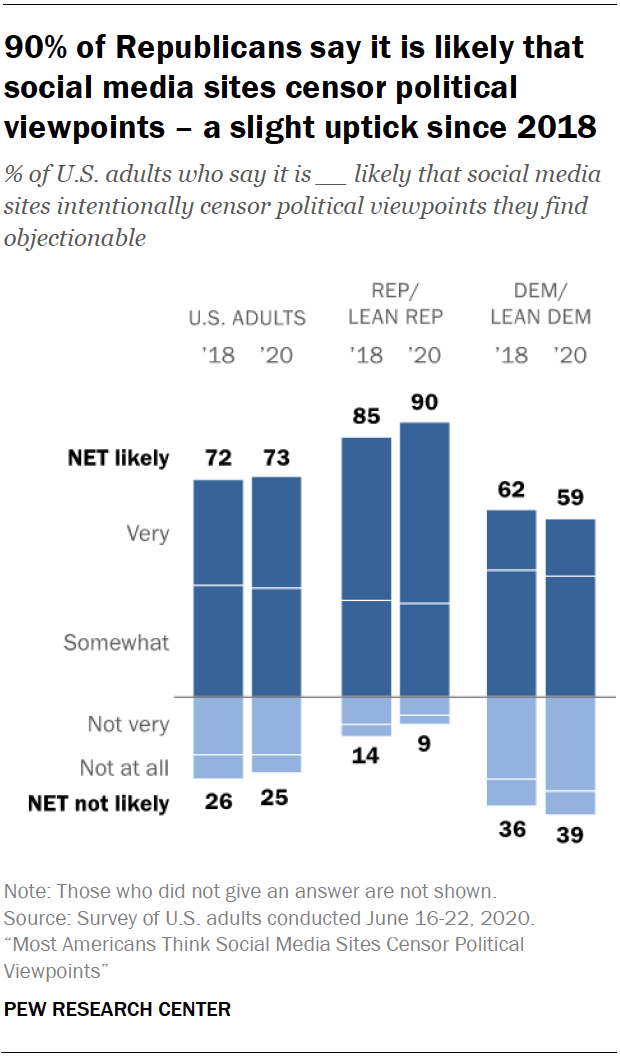
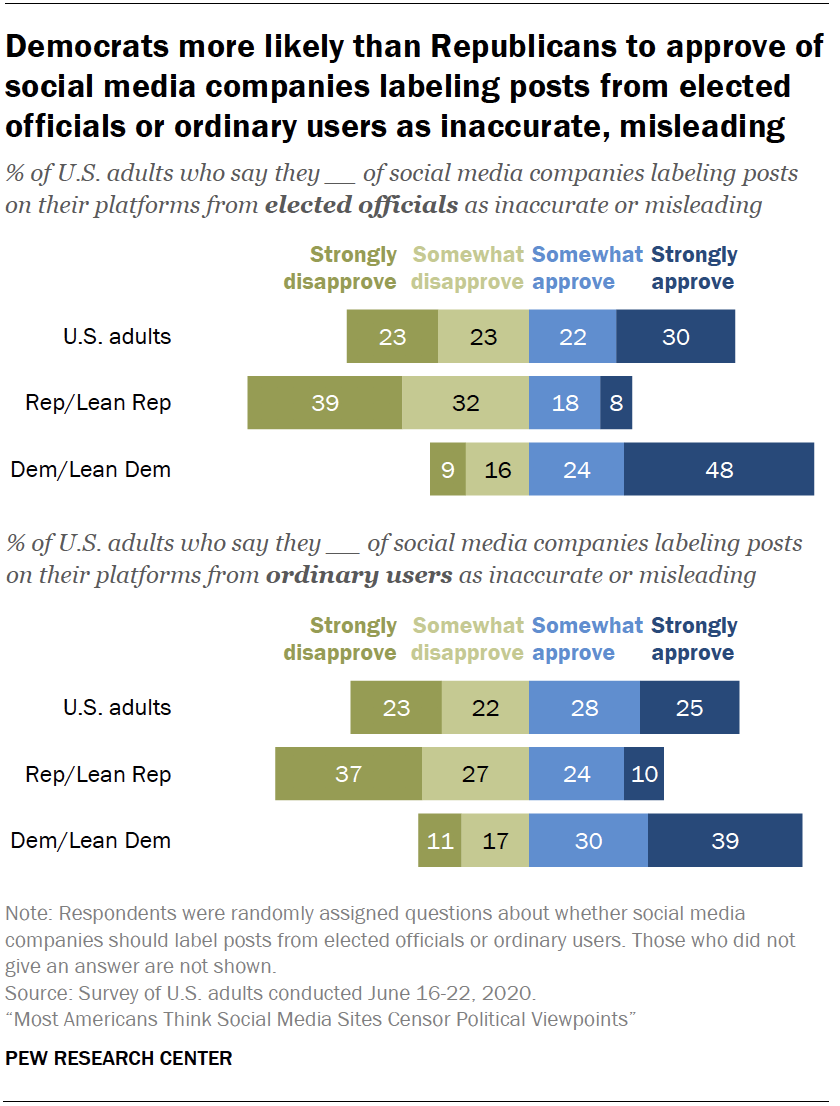
The debate over internet censorship is a complex and multifaceted issue that has sparked considerable controversy and debate in recent years. On one side of the debate are those who argue that internet censorship is necessary to protect children from inappropriate or harmful content, to prevent the spread of hate speech and misinformation, and to protect national security. On the other side are those who argue that internet censorship violates the principles of free speech and the open exchange of ideas, and that it can be used to suppress dissent and silence marginalized voices.
One argument in favor of internet censorship is that it can protect children from inappropriate or harmful content. Children are often more vulnerable to the negative effects of online content, such as cyberbullying, exposure to explicit material, and the risk of online predators. As a result, many argue that it is necessary to implement measures to protect children from these types of content, such as age restrictions, content filters, and parental controls.
Another argument in favor of internet censorship is that it can help to prevent the spread of hate speech and misinformation. Hate speech and misinformation can have serious real-world consequences, such as inciting violence or undermining democratic processes. As a result, many argue that it is necessary to censor this type of content in order to promote a safer and more informed online environment.
A third argument in favor of internet censorship is that it can protect national security. Governments often censor certain websites and information in order to prevent the spread of sensitive or classified information that could compromise national security. While this may be necessary in some cases, it can also be used to suppress dissent and stifle freedom of expression.
However, there are also strong arguments against internet censorship. One of the main arguments against internet censorship is that it violates the principles of free speech and the open exchange of ideas. The internet has become a vital platform for the exchange of ideas and the free flow of information, and censorship can undermine this essential function. In addition, censorship can be used to suppress dissent and silence marginalized voices, particularly in authoritarian regimes.
Another argument against internet censorship is that it is often ineffective and can be easily bypassed. Many people use virtual private networks (VPNs) or other methods to access censored content, and these measures are often difficult to enforce. As a result, censorship may be more of a symbolic gesture than an effective means of controlling access to information.
In conclusion, the debate over internet censorship is a complex and multifaceted issue that raises important questions about freedom of expression, the protection of children and national security, and the role of the internet in society. While there are valid arguments on both sides of the debate, it is important to carefully consider the potential consequences of censorship and to strike a balance between the competing demands of free speech and the need for some forms of regulation.