Key points of the treaty of versailles. The Treaty of Versailles Facts for Kids 2022-12-30
Key points of the treaty of versailles
Rating:
8,8/10
447
reviews
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed at the end of World War I in 1919 between the Allied Powers and Germany. The treaty was meant to officially end the war and establish the terms under which Germany would be required to pay reparations for damages caused by the conflict.
One of the key points of the Treaty of Versailles was the issue of war guilt. The treaty officially held Germany responsible for the outbreak of World War I and imposed heavy reparations on the country. Germany was required to pay billions of dollars in damages to the Allied Powers, including France, Britain, and the United States. This was seen as a way of punishing Germany for starting the war and making it financially difficult for the country to rebuild its military in the future.
Another key point of the Treaty of Versailles was the redrawing of national borders in Europe. The treaty resulted in the breakup of several empires, including the Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman empires, and the creation of new independent states in Eastern Europe. The treaty also resulted in the loss of territory for Germany, with the country losing control of areas such as Alsace-Lorraine to France and parts of Poland to the newly-created state of Czechoslovakia.
The Treaty of Versailles also established the League of Nations, an international organization dedicated to promoting international cooperation and resolving disputes peacefully. The League of Nations was seen as a major step forward in international relations and was seen as a way of preventing future wars.
One of the most controversial aspects of the Treaty of Versailles was the disarmament clause, which required Germany to significantly reduce its military capabilities. The treaty limited the size of the German army and navy and prohibited the country from developing certain types of weapons, such as tanks and chemical weapons. This was seen as a way of ensuring that Germany would not be able to threaten its neighbors in the future.
Overall, the Treaty of Versailles was a complex and multifaceted document that had a significant impact on the political landscape of Europe in the aftermath of World War I. While it was meant to bring an end to the conflict and promote stability, it also had far-reaching consequences that would shape the course of history for decades to come.
Treaty of Versailles: Definition, Terms, Dates & WWI

The treaty forced Germany to disarm, make substantial territorial concessions, and pay reparations to certain countries that had formed the Entente powers. President Woodrow Wilson was an early advocate of this philosophy. Germany had not taken part in the Conference. The Hall of Mirrors, where the signing took place, had also witnessed the crowning of Wilhelm I as king of a unified Germany in 1871. The new German democracy did not like the Versailles Treaty.
Next
The Fourteen Points of the Treaty of Versailles

The treaty established the League of Nations, which was a forerunner of the United Nations. The treaty required that Germany pay reparations for the damage it had caused during the war. The treaty had two main goals: to punish Germany for the war and to prevent another war from breaking out. China was the only nation present at Paris that did not sign the treaty. Many people in Germany felt that the treaty was too harsh, and that it was humiliating for their nation.
Next
10 facts about the Treaty of Versailles

Other people thought it is important to join the League because if other countries were fighting with each other, then the US could both be safe and not fight with them. Babies represent claims of the English, French, Italians, Polish, Russians, and enemy. Senate did not ratify any of the peace treaties and the U. Having unsuccessfully argued for the return of the Shantung Peninsula, a German colony seized by Japan during the war, the Chinese delegation refused to sign the treaty and left feeling betrayed by the West. Conscription was also forbidden and the German general staff was to be dissolved — officers who previously belonged to any formations of the army who were not retained in the units allowed to be maintained were forbidden to take part in any military exercise, whether theoretical or practical Article 175. This meant that the treaty lacked the support of one of the major powers in Europe, and made it more difficult to enforce. Establishment of the League of Nations American President Woodrow Wilson instructed Edward M.
Next
What were the 3 main points of the Treaty of Versailles?

Its primary goals, as stated in its Covenant, included preventing wars through collective security and disarmament and settling international disputes through negotiation and arbitration. Another alternative French policy was to seek a resumption of harmonious relations with Germany. German delegates in Versailles: Professor Walther Schücking, Reichspostminister Johannes Giesberts, Justice Minister Otto Landsberg, Foreign Minister Ulrich Graf von Brockdorff-Rantzau, Prussian State President Robert Leinert, and financial advisor Carl Melchior. Germany was not given the opportunity to participate in the negotiations, even after requests. Their job was to study Allied and American policy in virtually every region of the globe and analyze economic, social, and political facts likely to come up in discussions during the peace conference. The problems that arose from the treaty would lead to the Locarno Treaties, which improved relations between Germany and the other European Powers, and the renegotiation of the reparation system resulting in the Dawes Plan, the Young Plan, and the indefinite postponement of reparations at the Lausanne Conference of 1932. France and Britain, on the other hand, already controlled empires, wielded power over their subjects around the world, and still aspired to be dominant colonial powers.
Next
Treaty of Versailles summary/Main points/Consequences

Open diplomacy: President Wilson proposed that there be no private agreements between countries and that diplomacy was to proceed frankly and in public view. It took place in Paris during 1919 and involved diplomats from more than 32 countries and nationalities, including some non-governmental groups, but the defeated powers were not invited. This meant that during the early interwar period, the League played little part in resolving the turmoil resulting from the war. What were the key points of the Treaty of Versailles? Germany was not allowed to have an air force Neither military or naval air forces were allowed under Article 198, which also required Germany to hand over all aerial related materials. Provided by: Wikimedia Commons. The Treaty also factored into I cannot imagine any greater cause for future war that that the German people…should be surrounded by a number of small states… each containing large masses of Germans clamouring for reunion. He was a major player at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919 that reordered Europe after the defeat of the Central Powers.
Next
Treaty Of Versailles Key Facts

Italy sent Vittorio Orlando. Still, many people voted for them because of their promises like helping with reparations and fighting inflation. Germans were mad about the treaty, they thought it was just another way for people to tell them what to do. Independence of Austria-Hungary: Austria-Hungary to be allowed to continue existing as an independent country and its people be accorded free opportunity for development. In doing so, Wilson ultimately began to lead the foreign policy of the United States toward interventionism, a move strongly resisted in some domestic circles.
Next
The Treaty of Versailles

The treaty was written by the Allies, who were the victors of World War I. In 1923, Germany had a lot of hyperinflation too much inflation which made things harder for the German economy. This date was alsoimbued with significance in Germany as the anniversary of the establishment of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701. The League lasted for 26 years; the United Nations UN replaced it after the end of the Second World War in April 1946 and inherited a number of agencies and organizations founded by the League. The treaty was written by the leaders of the Allied Powers: the United States, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Japan. Consequences The Treaty of Versailles was also called The Peace without Victory because it was meant to be peace, but not a victory like Woodrow Wilson wanted.
Next
What were the 5 main points of the Treaty of Versailles?
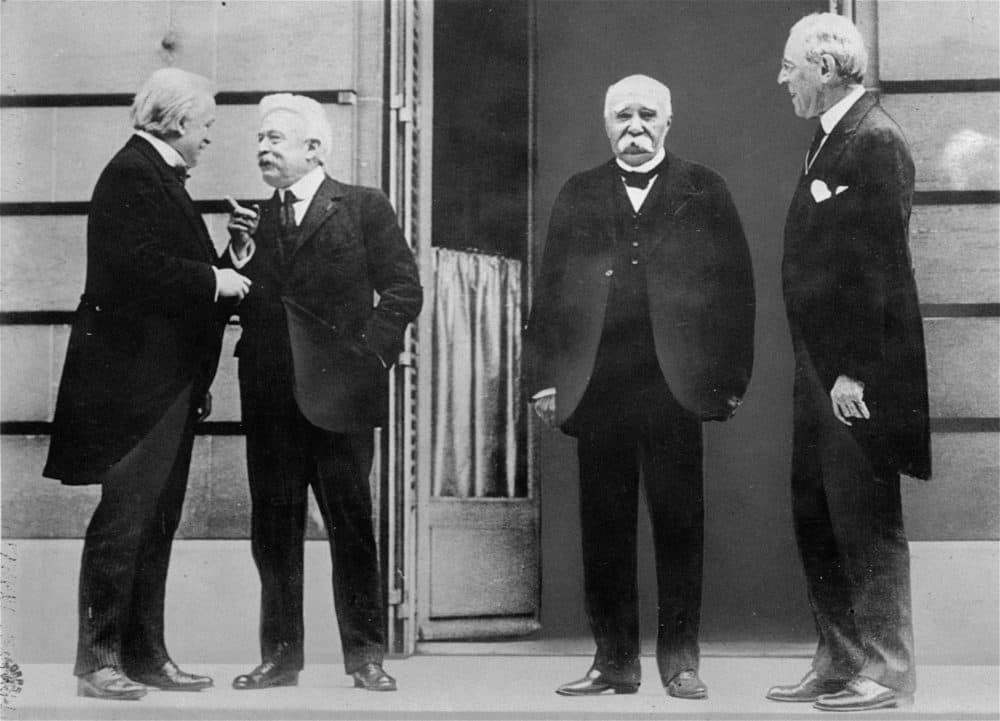
They met informally 145 times and made all the major decisions, which in turn were ratified by the others. The other Central Powers on the German side of World War I signed separate treaties. The Fourteen Points In January 1918, Woodrow Wilson talked about peace and how the world should be. The third key point was that the treaty allowed for the creation of the League of Nations. He demanded Congressional control of declarations of war; Wilson refused and blocked his move to ratify the treaty with reservations. In the Middle East, negotiations were complicated by competing aims, claims, and the new mandate system. Leading a Congress in Democratic hands, he oversaw the passage of progressive legislative policies unparalleled until the New Deal in 1933.
Next







