Interest groups are organizations that seek to influence public policy and decision-making on behalf of a specific cause or set of issues. These groups often use various techniques and tactics to achieve their goals, including lobbying. Lobbying refers to the act of attempting to influence decisions made by government officials, typically by private interest groups, organizations, or individuals.
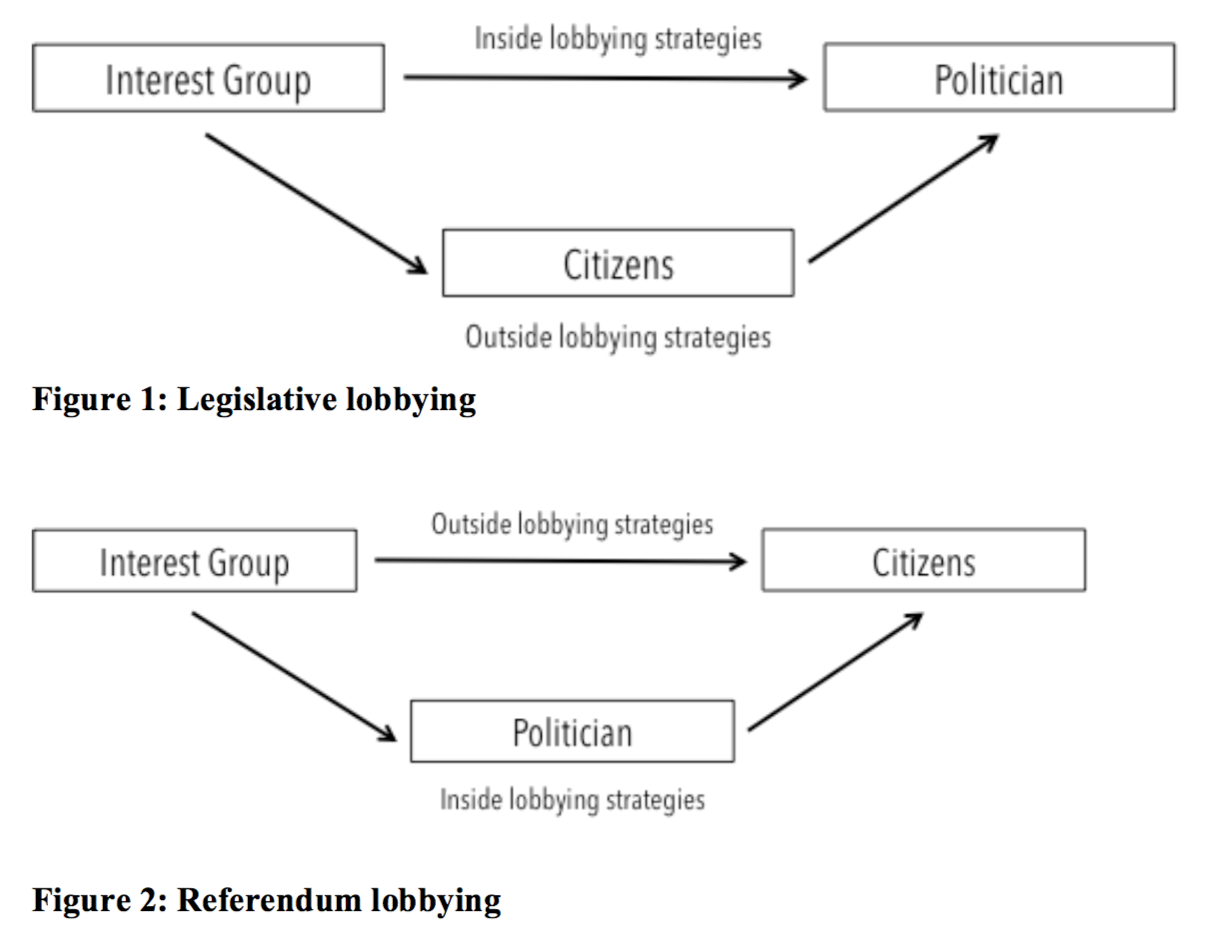
There are several different types of lobbying techniques that interest groups may use. One common technique is direct lobbying, which involves directly communicating with lawmakers and other government officials to advocate for or against specific policies or legislation. This can take many forms, such as meeting with lawmakers in person, sending letters or emails, or making phone calls.
Another common lobbying technique is grassroots lobbying, which involves mobilizing the general public to support a particular cause or issue. This can involve organizing rallies or protests, using social media to spread the group's message, or contacting legislators and government officials to voice support for a particular cause.
Another technique that interest groups may use is media advocacy, which involves using the media to publicize a cause or issue and to persuade the public and lawmakers to support it. This can include placing articles in newspapers or magazines, producing public service announcements, or appearing on television or radio to discuss the group's issues.
In addition to these techniques, interest groups may also use campaign contributions as a way to influence legislators and other government officials. This can involve making direct contributions to politicians' campaigns or to political parties, or using independent expenditure committees to support candidates who align with the group's interests.
Lobbying can be a powerful tool for interest groups to influence public policy and decision-making. However, it can also raise concerns about the influence of special interests and the potential for corruption. In response to these concerns, many countries have laws regulating lobbying activities, such as requiring lobbyists to register and disclose their activities, and placing limits on campaign contributions.
In conclusion, lobbying is a technique used by interest groups to influence public policy and decision-making. There are many different forms of lobbying, including direct lobbying, grassroots lobbying, media advocacy, and campaign contributions. While lobbying can be a valuable tool for advancing the interests of certain groups, it can also raise concerns about the influence of special interests and the potential for corruption.