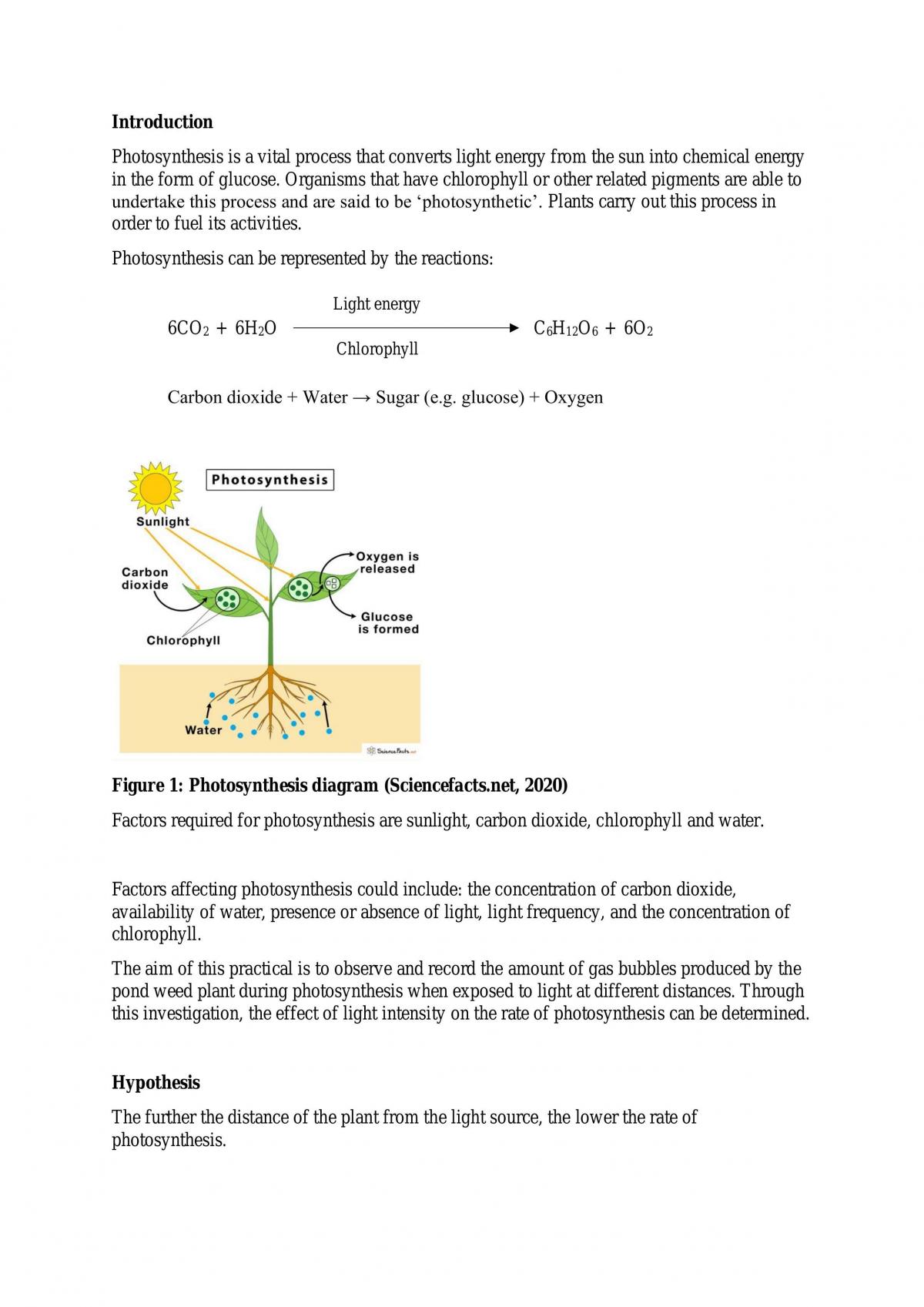
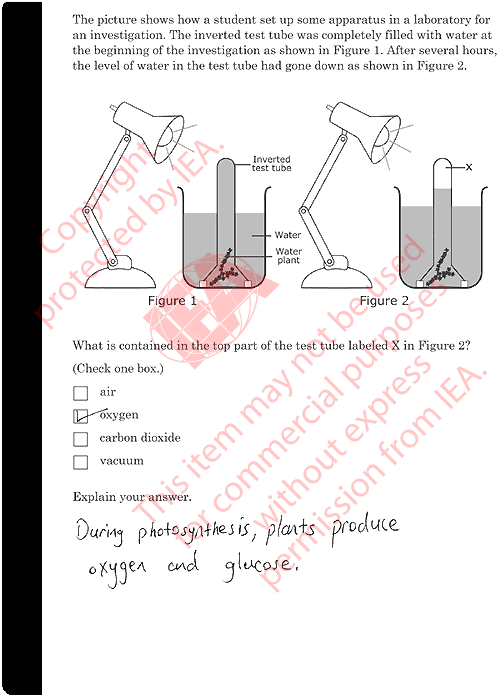
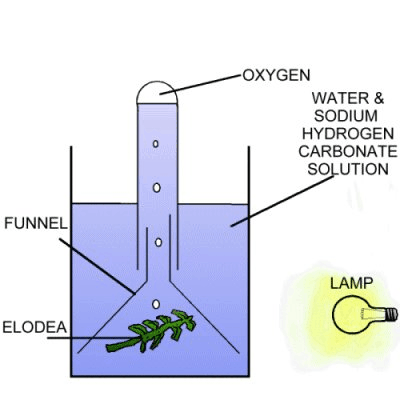
Photosynthesis is a process that occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria, in which energy from sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (a sugar) and oxygen. This process is critical for the survival of plants, as it allows them to produce the energy they need to grow and thrive. It is also important for the overall health of the planet, as it helps to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and produce oxygen, which is essential for animal life.
One practical application of photosynthesis is in the field of agriculture. Farmers rely on photosynthesis to produce crops, which are the primary source of food for humans and animals. Photosynthesis is also important for the production of biofuels, which are alternative sources of energy that are derived from plant materials.
Photosynthesis can also be studied in the laboratory setting, where scientists can manipulate various factors such as light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide levels to understand how they impact the process. This can help researchers develop ways to improve crop yields and increase the efficiency of biofuel production.
In addition to its practical applications, photosynthesis is also an important topic of study in the field of biology. It helps scientists understand the fundamental processes that sustain life on Earth and how different organisms interact with their environment.
Overall, photosynthesis is a vital process that plays a crucial role in many aspects of our lives. From producing the food we eat and the oxygen we breathe, to providing alternative sources of energy, it is an essential component of the natural world that we rely on every day.