A classification essay is a type of academic writing that organizes and categorizes ideas or objects into specific groups or categories. The purpose of this type of essay is to provide a clear and logical structure for presenting information, making it easier for the reader to understand and process.
There are many different ways to write a classification essay, and the specific approach will depend on the topic and the purpose of the essay. However, there are a few common elements that are typically included in this type of essay.
One of the key elements of a classification essay is the use of clear and concise categories or groups. These categories should be based on a logical principle, such as shared characteristics or common features. It is important to ensure that the categories are mutually exclusive and exhaustive, meaning that they should cover all of the possible options and not overlap with one another.
Another important element of a classification essay is the use of examples to support and illustrate the categories. These examples should be relevant and specific, and they should help to clarify and reinforce the points being made in the essay.
Here are a few examples of classification essay topics and the categories that could be used to organize the information:
Types of pets: This topic could be organized into categories such as dogs, cats, birds, small mammals, and reptiles. Each category could include examples of different breeds or species within that group.
Forms of transportation: This topic could be organized into categories such as cars, buses, trains, planes, and bikes. Each category could include examples of different types of vehicles within that group, such as different makes and models of cars.
Types of music: This topic could be organized into categories such as rock, pop, hip hop, classical, and jazz. Each category could include examples of different artists or styles within that group.
Overall, a classification essay is a useful tool for organizing and presenting information in a clear and logical way. By using clear categories and relevant examples, it is possible to effectively convey complex ideas and information to the reader.
Diktat is a German word that means "dictation" or "dictatorship." It is often used to refer to the harsh terms imposed on a defeated country by the victors in a war. In the context of Germany, the term diktat is most commonly associated with the Treaty of Versailles, which was signed at the end of World War I in 1919.
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty between the Allied Powers (led by France, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and Germany. It was meant to bring an end to the war and to establish the terms under which the defeated Germany would be forced to pay reparations to the Allied Powers. The treaty also imposed severe limitations on Germany's military and territorial expansion.
Many Germans viewed the Treaty of Versailles as a diktat, or dictate, because they felt that the terms were imposed on them by the victorious Allies without any input from the German government or people. The treaty was seen as extremely harsh and punitive, and many Germans felt that their country had been humiliated and treated unfairly.
The resentment and anger that many Germans felt towards the Treaty of Versailles played a significant role in the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in the 1920s and 1930s. Hitler and the Nazis promised to restore Germany's honor and power, and they used the treaty as a rallying cry to mobilize support for their cause. Hitler came to power in 1933, and he quickly set about tearing up the Treaty of Versailles and rebuilding the German military. This ultimately led to World War II, which ended with the defeat of Germany and the imposition of another set of harsh terms in the form of the Potsdam Agreement.
In conclusion, the term diktat is closely associated with the Treaty of Versailles and its impact on Germany following World War I. Many Germans saw the treaty as a dictate imposed on them by the victorious Allies, and the resentment and anger that it generated played a significant role in the rise of the Nazi Party and the outbreak of World War II.
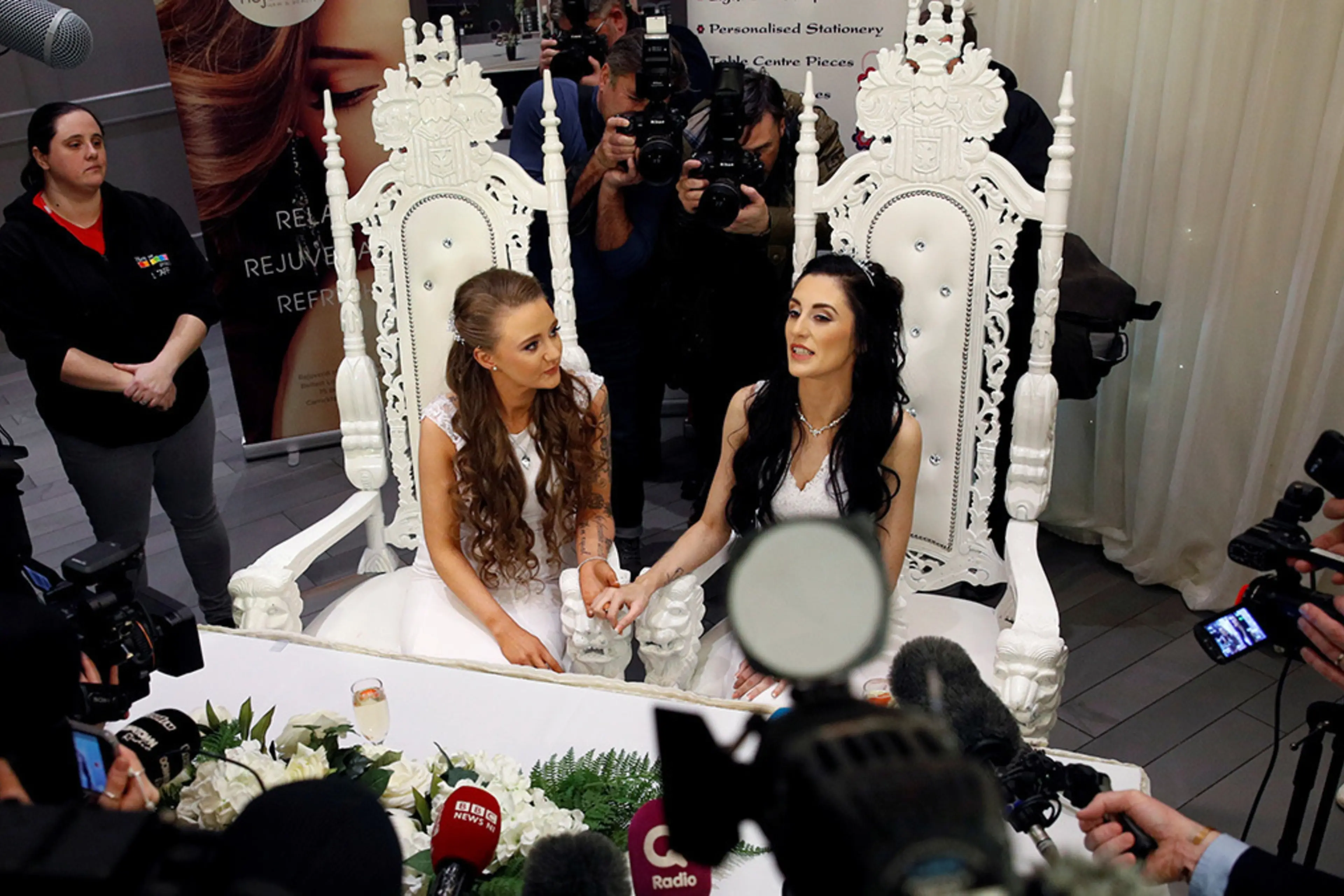
The debate over same-sex marriage is a controversial and highly divisive issue that has been at the forefront of political and social discourse for many years. On one side of the argument are those who believe that marriage should be defined as a union between one man and one woman, and that any attempt to redefine it is a threat to the traditional values of society. On the other side are those who believe that same-sex couples have the same right to marry as heterosexual couples, and that denying them this right is a form of discrimination and a violation of their human rights.
The arguments in favor of same-sex marriage often center on the idea that it is a fundamental right that should be extended to all people, regardless of their sexual orientation. Proponents argue that denying same-sex couples the right to marry is a form of discrimination and violates the principles of equality and justice. They point out that marriage is a legally recognized institution that confers a wide range of benefits, including tax advantages, spousal support, and the ability to make medical decisions for a partner. Denying these benefits to same-sex couples, they argue, is unfair and denies them equal protection under the law.
Opponents of same-sex marriage often argue that it goes against the traditional definition of marriage and the natural order of things. They may claim that marriage is intended for the purpose of procreation and that same-sex couples are unable to have children together. They may also argue that same-sex marriage threatens the institution of marriage and the stability of society as a whole.
However, these arguments have been widely debunked. Same-sex couples can adopt children and raise families, and there is no evidence to suggest that same-sex marriage has any negative impact on the institution of marriage or on society as a whole. In fact, many studies have shown that same-sex couples are just as capable of creating stable, loving relationships as heterosexual couples.
Another argument often used against same-sex marriage is the idea that it goes against religious beliefs. Opponents may claim that same-sex marriage is against the teachings of their religion and that it should not be allowed in a society that is predominantly religious. However, this argument ignores the fact that the United States is a secular society and that the government should not be making decisions based on the religious beliefs of one group.
Ultimately, the debate over same-sex marriage is about whether or not all people should have the same rights and opportunities, regardless of their sexual orientation. While opponents may argue that same-sex marriage goes against traditional values and threatens the stability of society, the evidence suggests that allowing same-sex couples to marry would not have any negative impact and would simply provide them with the same rights and benefits as heterosexual couples. It is important for society to recognize and respect the rights of all individuals, including the right to marry the person they love.