Soil investigation works are an important part of the design and construction process for many types of projects, including buildings, bridges, roads, and other infrastructure. These works involve the collection and analysis of soil samples from a site in order to determine the properties and characteristics of the soil at that location. This information is used to design foundations, slopes, and other elements of the project in a way that is safe and stable.
There are several methods that can be used for soil investigation works, depending on the type of project and the specific needs of the site. Some common methods include drilling, boring, and test pit excavation.
Drilling involves the use of a machine or hand-held drill to extract soil samples from the ground. The drill can be either rotary or percussion, depending on the type of soil and the depth of the sample being collected. Boring is similar to drilling, but uses a continuous auger to extract a series of soil samples at different depths. Test pit excavation involves the manual excavation of a small pit in the ground to expose and sample the soil.
Once the soil samples have been collected, they are typically analyzed in a laboratory to determine their physical and chemical properties. This can include tests for pH, nutrient content, moisture content, and other factors that can affect the stability and suitability of the soil for the intended use.
The results of the soil investigation works are typically compiled in a report, which is used by the design team to inform the design of the project. The report may include recommendations for soil treatment or modification, as well as guidance on the design and construction of foundations, slopes, and other elements of the project.
In addition to the physical and chemical analysis of the soil, soil investigation works may also involve the assessment of potential environmental impacts, such as the presence of hazardous materials or the potential for soil erosion.
Overall, soil investigation works are a vital part of the design and construction process, providing important information that helps to ensure the stability and safety of the finished project.
Soil Investigations for Building Foundations
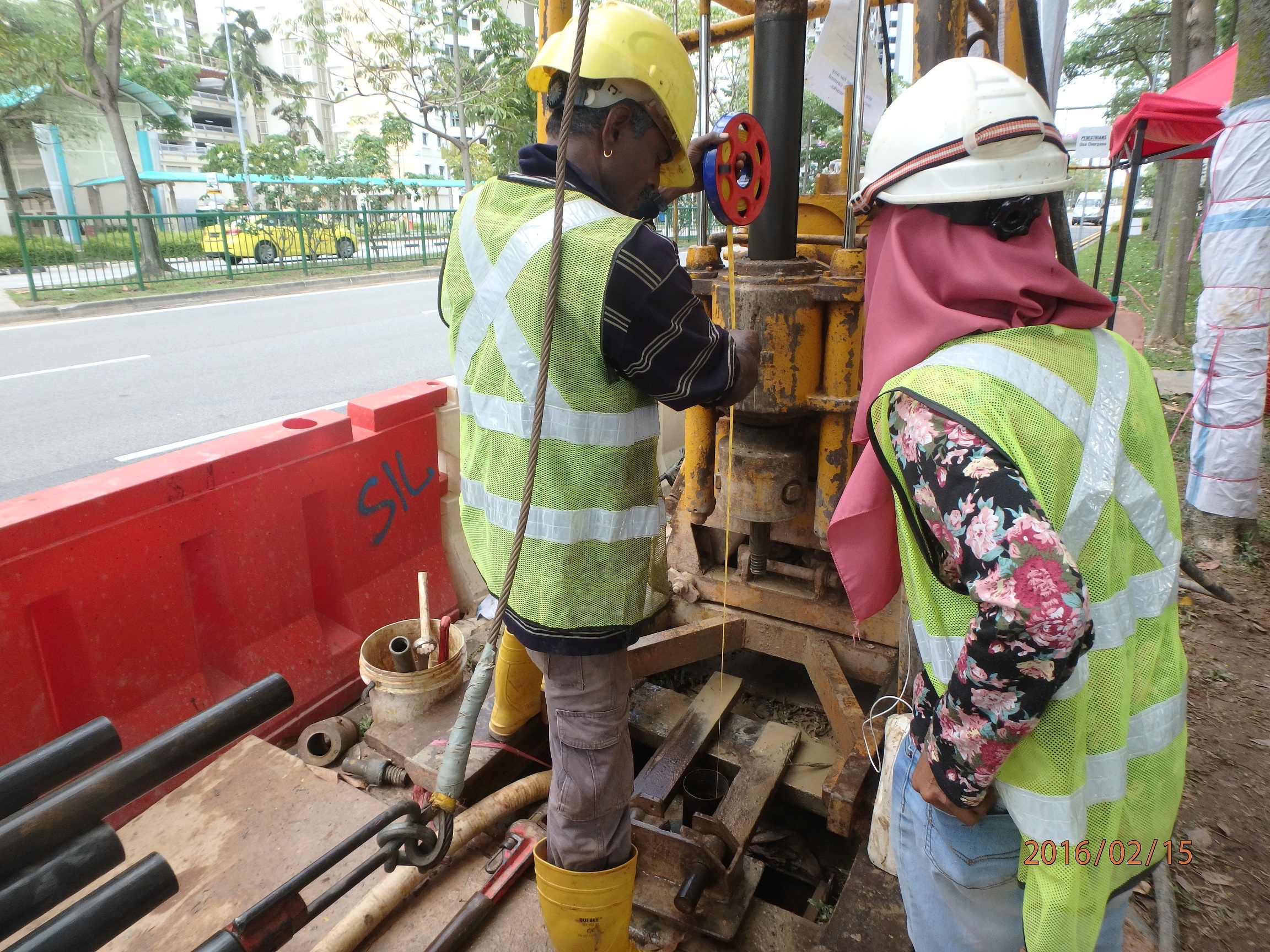
Design factors governing the degree of disturbances: i. Therefore, the structural engineers can efficiently and accurately design the structural elements for the long-term viability and soundness of the project. The drilling fluid is used to cool the drill bit, remove the cuttings, and flush them up the borehole outside the core barrel. When N is greater than 15, Terzaghi and Peck have recommended the use of an equivalent penetration resistance, Ne in place of the actually observed value of N. Site works usually consist of the Cone Penetration Test, Vane Shear Test, Standard Penetration Test , Installation of Water Standpipe, Instrumentations, etc.
Soil Investigation Companies

Sampling locations should be limited to areas at least 50 feet from lanes, fence rows, Barnes, and roads. Preliminary Site Exploration Preliminary site exploration is carried out for small projects, light structures, highways, airfields, etc. Environmental soil investigations, soil samples are collected at locations specified in the previous assessment or at sites likely to have been the source areas for the suspected releases. After which the drilling rigs shall be mobilized to the particular location. Intermediate boreholes should be drilled if required. The bearing capacity can be determined in the field and also from the results of tests conducted in the laboratory on the soil samples. Cone penetration test or Dutch cone test This type of test is carried out to get a continuous record of the resistance of the soil by penetrating steadily under static pressure, a cone with base of 10 sq.
SOIL INVESTIGATION FOR MAJOR WORKS IN MES

The ground information profile obtained from borehole drilling can also be enhanced by Geophysical Survey which is one of the strong specialized fields of Ryobi-G. An experienced workman can assess the nature of the soil by observing the way the rod is penetrated into the soil. Water removal contracts the soil during the dry season. Without it, any design parameters adopted or assumptions made by the Engineer with regards to the ground earthwork, foundation system, slopes, retaining walls, etc. The jack-up barges, with tug boats in attendance, will have a circular safety working zone of 30 meters radius centred at the barges. The extent of investigation depends on whether the area is built up or not and the size of the structure. In addition, water expands when frozen in the soil, causing heaving and cracking of walls and floor slabs.









