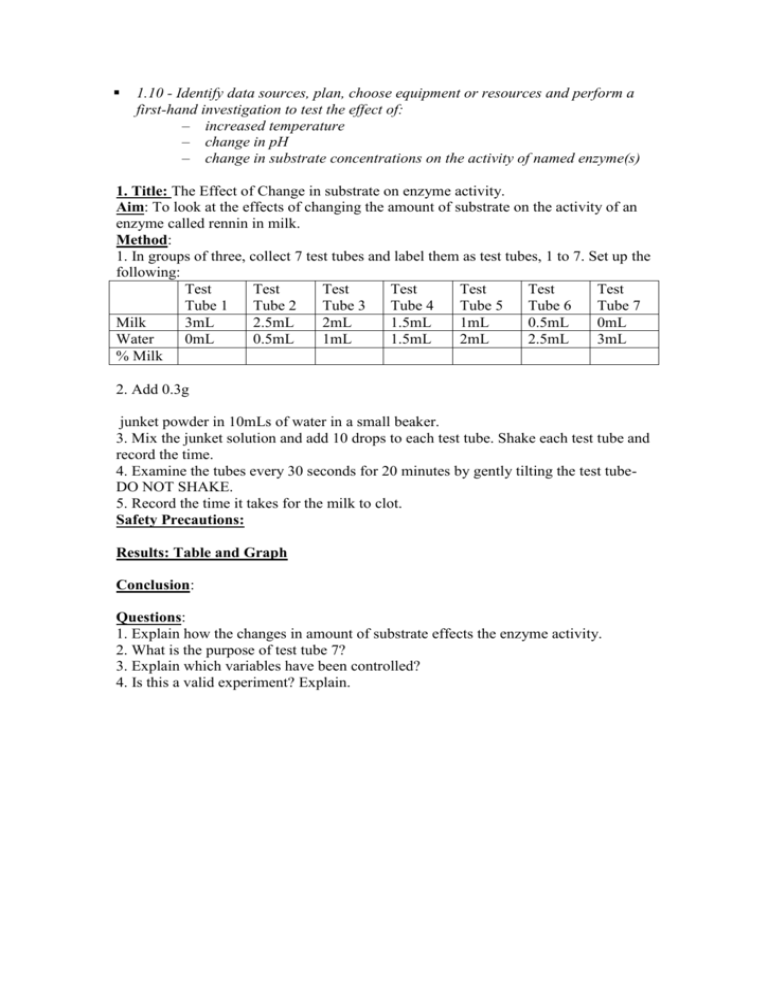
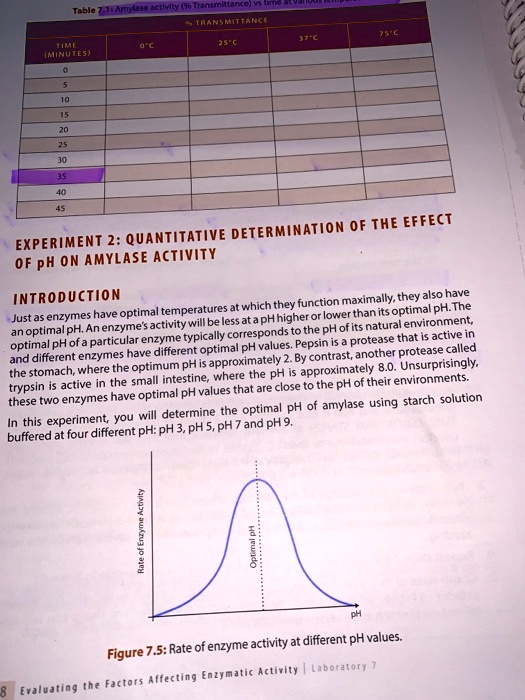
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms. They are essential for many biological processes, including digestion, metabolism, and cellular respiration. Enzyme activity, or the rate at which an enzyme catalyzes a reaction, can be affected by various factors, including temperature, pH, and substrate concentration. In this essay, we will focus on the effect of pH on enzyme activity.
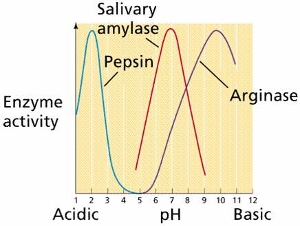
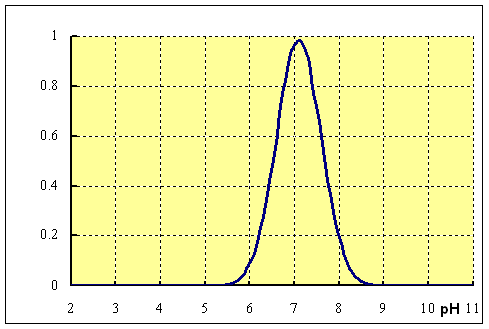
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution. It is calculated on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, lower values indicating increasing acidity, and higher values indicating increasing basicity. Most enzymes have an optimal pH at which they are most active. For example, the enzyme pepsin, which is involved in digestion, has an optimal pH of around 1.5, while the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose, has an optimal pH of around 6.
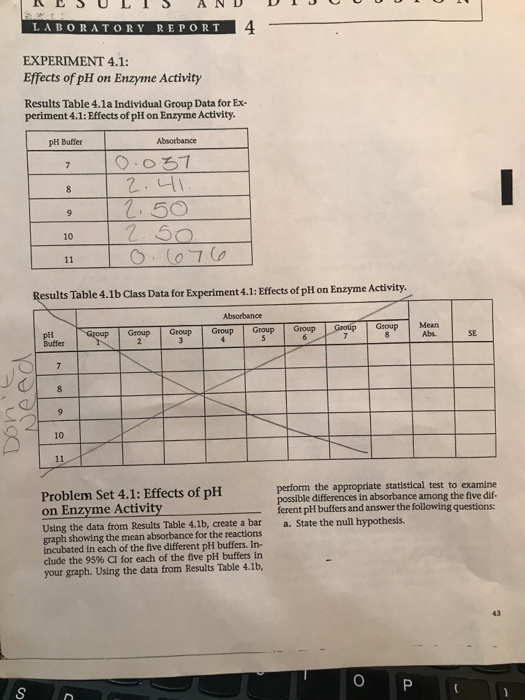
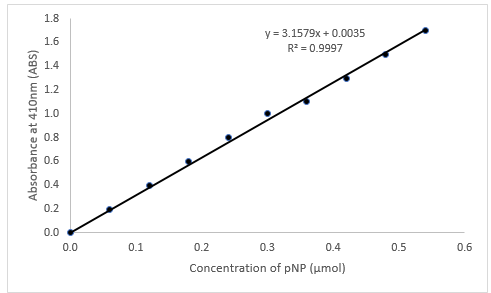
To study the effect of pH on enzyme activity, researchers often use a laboratory experiment in which they vary the pH of the solution containing the enzyme and measure the resulting enzyme activity. This can be done using a spectrophotometer, which measures the amount of light absorbed by a solution and can be used to quantify the rate of a chemical reaction.
In general, enzymes are sensitive to changes in pH and can become denatured, or lose their three-dimensional structure, at extreme pH values. When the pH of a solution is too far from an enzyme's optimal pH, the enzyme will denature and become inactive. This is because the ionization of amino acid residues in the enzyme's active site, which is responsible for catalyzing the reaction, can be affected by changes in pH.
For example, consider the enzyme catalase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide. If the pH of the solution containing catalase is too high or too low, the enzyme will denature and the reaction will not occur. However, if the pH is within a certain range, the enzyme will remain active and the reaction will proceed at a faster rate.
In conclusion, the effect of pH on enzyme activity is significant because it can significantly alter the three-dimensional structure of enzymes and their ability to catalyze reactions. Understanding this effect is important for a variety of applications, including medicine, agriculture, and industrial processes. By studying the effect of pH on enzyme activity, researchers can better understand the role of enzymes in living organisms and design strategies to optimize enzyme activity for various purposes.