The law of diminishing returns can explain why. GEOG 1101 Chapter 2 Flashcards 2022-12-31
The law of diminishing returns can explain why
Rating:
4,2/10
492
reviews
Writing a thesis paper can be a daunting task, especially if you have never written one before. However, with a clear understanding of the steps involved and a little bit of planning, you can successfully write a thesis paper that is both informative and well-written. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write a thesis paper:
Choose a topic: The first step in writing a thesis paper is to choose a topic that is both interesting and relevant to your field of study. It should be something that you are passionate about and that you have a good understanding of.
Develop a thesis statement: Once you have chosen your topic, it is time to develop a thesis statement. This is a one-sentence summary of the main point of your paper. It should be clear and concise, and it should accurately reflect the focus of your paper.
Conduct research: The next step is to conduct research on your topic. This may involve reading articles, books, and other sources of information. Make sure to take thorough notes and record the sources of your information so that you can properly cite them in your paper.
Create an outline: An outline is a roadmap for your paper that helps you organize your thoughts and ideas. Start by creating an outline that includes the main points you want to cover in your paper. Then, break these points down into smaller subpoints and arrange them in a logical order.
Write your paper: Now it is time to start writing your paper. Begin by introducing your topic and explaining the purpose of your paper. Then, present your main points, using evidence and examples to support your arguments. Be sure to include in-text citations whenever you quote or paraphrase a source.
Edit and revise: After you have finished writing your paper, it is important to spend some time editing and revising. This may involve checking for grammar and spelling mistakes, rephrasing awkward sentences, and ensuring that your paper flows logically and cohesively.
Submit your paper: Once you have finished editing and revising your paper, it is time to submit it. Be sure to follow any guidelines provided by your instructor or supervisor, and double-check that you have properly formatted your paper and included all necessary citations.
By following these steps, you can write a clear and well-written thesis paper that effectively communicates your ideas and arguments. Remember to give yourself plenty of time to research, write, and revise, and don't be afraid to seek help if you need it. With a little bit of effort and dedication, you can successfully complete your thesis paper and move on to the next stage of your academic journey.
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns: Definition, Example, Use in Economics
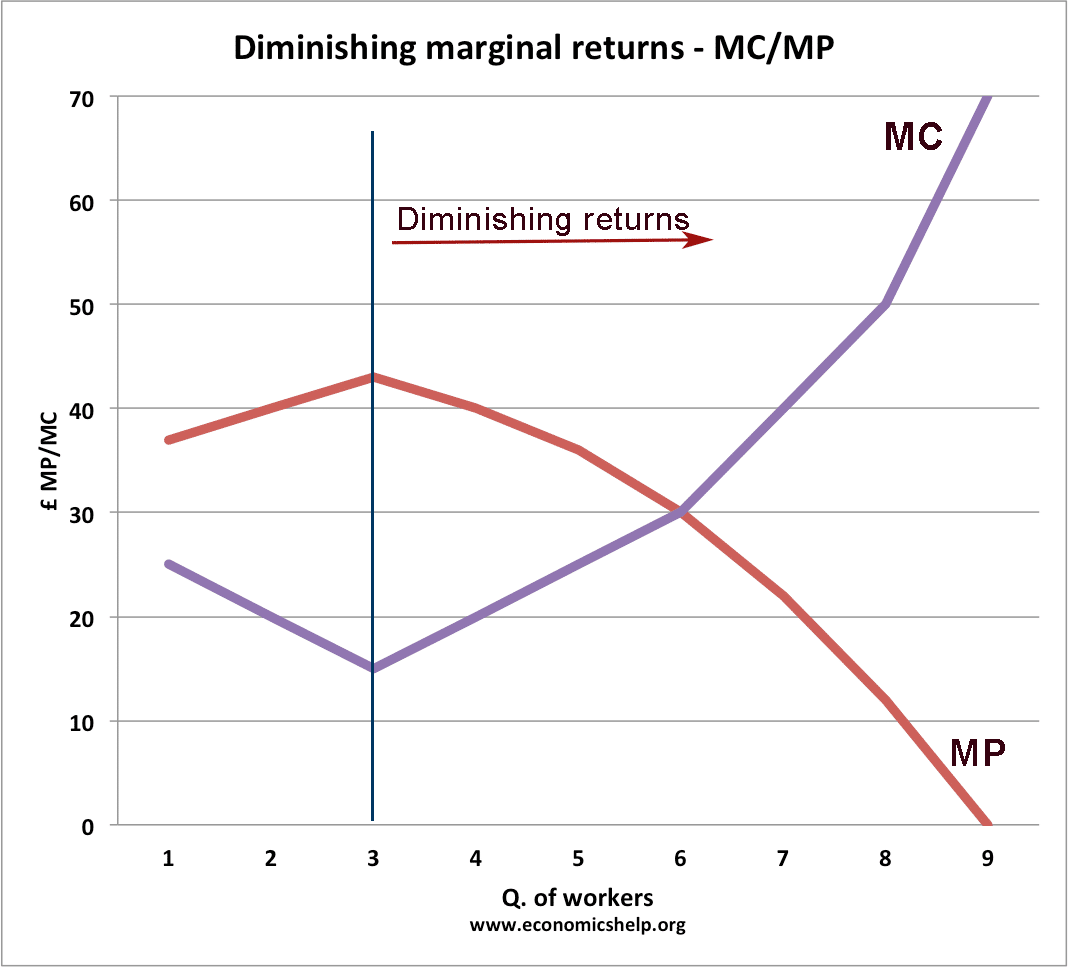
Among these factors, one of the most important factors for the law of increasing returns is fixed capital. Diminishing marginal returns primarily looks at changes in variable inputs and is therefore a short-term metric. This is because all factors are variable in the long-run. The above diagram represents the law in the intensive form. Therefore, it cannot be applied universally. Yes, this production function exhibits diminishing returns to labor.
Next
Please explain why the law of diminishing returns applies only in the short
Because labor is the only variable input and its price its wage rate is constant, MC is found by dividing the wage rate by MP. Hence there are increasing returns. If we can obtain some and cannot obtain others, the proportion in which we combine the factors becomes defective, and the returns begin diminishing. ADVERTISEMENTS: Statement of the Law: Every farmer knows by experience that, if a particular piece of land is cultivated over and over again, it generally yields less than proportionate returns. Why is the law of diminishing marginal utility applicable only in the short run? This leads to an increase in the number of workers to compensate the decrease in capital and capital-labor ratio. In other words, the total output initially increases with an increase in variable input at given quantity of fixed inputs, but it starts decreasing after a point of time.
Next
GEOG 1101 Chapter 2 Flashcards

Stage III: Refers to the stages in which the total product starts declining with an increase in number of workers. You might be interested: What kind of law should i practice What is meant by returns to a factor? The opposite is true when economic profit is negative. Until and unless these defects are remedied, the agricultural yield in India will not compare favorably with that of other countries. For example, if the capital-labour ratio is 2:6 and capital is indivisible and labor hired is less than six, then capital is unutilized. Thus, for a few years in the beginning, the returns will be more than proportionate.
Next
The law of diminishing returns explains why
The law of diminishing returns is described by different economists in different ways, which are as follows: ADVERTISEMENTS: According to G. What is the law of diminishing returns quizlet? This means that total output will be increasing at a decreasing rate. If every year more, and still more, units of labour and capital are put into it, the successive return per unit does not increase, but actually decreases. Broadly speaking, this is true. Thus, the law of diminishing returns also applies where cultivation is carried on extensively. It applies equally to other extractive industries like fishing, mining and quarrying. But the law is not peculiar to agriculture.
Next
Law Of Diminishing Returns: With Limitations

Accordingly, with the increase of input, output increases at an increasing rate, then decreases, maximizes and starts to reduce. It measures by how much proportion the output changes when inputs are changed proportionately. Understanding the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns The law of diminishing marginal returns is also referred to as the "law of diminishing returns," the "principle of diminishing marginal productivity," and the "law of variable proportions. For some time, therefore, increased application of capital may bring in more than proportionate returns. In economics, the law of diminishing marginal utility states that the marginal utility of a good or service declines as its available supply increases.
Next
What is Diminishing Marginal Returns, Why Does It Occur?

Food supply does not keep pace with the increase in population simply because agriculture is subject to the law of diminishing returns. A good example of diminishing returns includes the use of chemical fertilisers- a small quantity leads to a big increase in output. Importance of the Law of Diminishing Returns in Economic Theory : This law is one of the most fundamental laws of Economics. What is short run production function? Why does the law only occur in the short run? Total Product TP is the total output produced by workers. For increasing the level of production, it can hire more workers.
Next
Does law of diminishing returns apply in the short run or long run?

This is the law of increasing cost. The MRP of different workers can be listed in a table and a graph can be formed from that table. This reduces the yield. The law of returns to a factor explains such a production function. It explains what happens to the output when the variable factor changes, keeping the fixed factors constant. The 6th dose makes no addition to the total, and the 7th even decreases it. Man is the master.
Next
Chapter 9 Costs of Production Flashcards

Why does law of diminishing returns hold in production in short run period? Law of diminishing returns helps mangers to determine the optimum labor required to produce maximum output. Law of Increasing Costs: The following diagram Fig. Further, it studies the change in output by varying the quantity of one input. Diminishing returns occur in the short run when one factor is fixed e. All factors of production, land, labour, capital or enterprise cannot be increased every time. The stage of diminishing returns in the case of total return, however, comes much later, and if the farmer is prudent, it may never come. In such a case, an organization would prefer to hire 20 workers to meet the optimum level of output in case if the labor is available at free of cost, which is not possible.
Next
Law of Diminishing Returns (Explained With Diagram)

But if, on the other hand, the farmer brings more and more land under cultivation, even then the returns will decrease. This adds to the cost. If long-run ATC drops quickly to its minimum point and then rises abruptly, the industry will likely be composed of many small firms. When does diminishing returns to Labour take place? The marginal product of labor, the extra output produced by each additional worker, diminishes as workers are added, and this starts to occur with the second unit of labor. In the short run, by definition, the scale of the plant cannot change: The firm cannot bring in more machinery or move to a larger building. Stage I: Refers to the stages of production in which the total output increases initially with the increase in number of labor table-3 shows the increase in marginal product till the number of workers increased to 10 and 11.
Next
Econ Exam 2 Flashcards
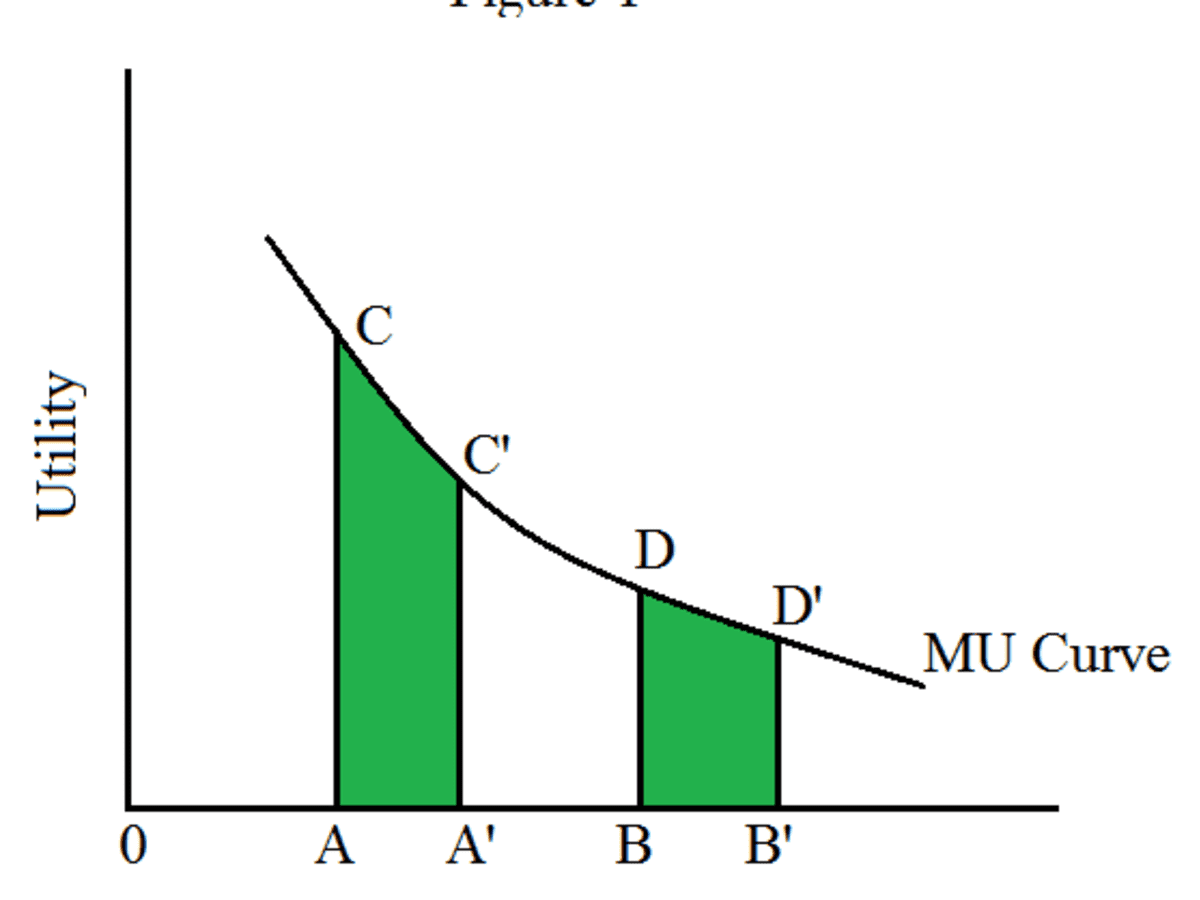
What does diminishing mean? This phenomenon is referred to as economies of scale. Optimal Employment of Labor : As shown in Table-3, when the number of workers is 20, then the output reaches to its maximum level. For example, suppose that there is a manufacturer that is able to double its total input, but gets only a 60% increase in total output; this is an example of decreasing returns to scale. The Law of Diminishing Returns also known as the law of Diminishing Marginal Returns states that in a production process, as we increase the quantity of one input which is combined with other fixed inputs, the marginal physical productivity of the variable input must eventually decline means that at a certain period of time, if a firm adds one additional factor of production to their operations with all things being equal, ceteris paribus, this may result in smaller increases in output despite the added resource. If economic profit is greater zero this implies the business venture is earning above average normal profits more than other alternative business ventures on average , thus more resources will flow towards this activity. Lack of cooperation results in the misuse of the machinery or waste of materials. ADVERTISEMENTS: iii The scope of division of labour is also limited.
Next









