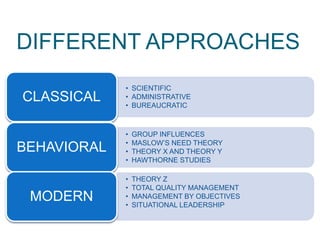
Management refers to the process of organizing and controlling the resources of an organization in order to achieve its goals and objectives. There are various approaches to management that have been developed over the years, each with its own set of characteristics and principles. These approaches are based on different assumptions about human behavior, decision-making, and organizational structure, and they have been used by managers in different contexts and industries to achieve success. In this essay, we will examine four major approaches to management: scientific management, bureaucratic management, human relations management, and contingency management.
Scientific management, also known as Taylorism, is an approach that emphasizes the use of scientific methods to analyze and improve work processes. It was developed by Frederick Winslow Taylor in the late 19th century and is based on the idea that there is one best way to perform a task, and that this way can be discovered through careful analysis and experimentation. The principles of scientific management include the use of time and motion studies to identify the most efficient way to perform a task, the division of labor to specialize workers and increase efficiency, and the use of incentives to motivate workers.
Bureaucratic management is an approach that emphasizes the importance of rules, procedures, and hierarchy in organizations. It was developed by Max Weber in the early 20th century and is based on the idea that organizations should be structured in a rational and efficient manner, with clear lines of authority and decision-making. The principles of bureaucratic management include the use of formalized rules and procedures to guide decision-making and behavior, the use of hierarchy to delegate authority and responsibility, and the use of specialized departments and divisions to organize and coordinate work.
Human relations management is an approach that emphasizes the importance of human factors in the workplace, such as motivation, communication, and leadership. It was developed in the 1930s and 1940s by researchers such as Elton Mayo and Abraham Maslow, and is based on the idea that people are more likely to be productive and satisfied if they feel valued and supported in the workplace. The principles of human relations management include the use of participative management and employee involvement to empower and engage workers, the use of communication and collaboration to build trust and understanding, and the use of leadership and motivation techniques to inspire and guide employees.
Contingency management is an approach that emphasizes the importance of adapting to the unique characteristics and needs of an organization or situation. It is based on the idea that there is no one best way to manage, and that the most effective approach will depend on the specific context in which the organization operates. The principles of contingency management include the use of situation analysis to identify the key factors that will influence the success of a management strategy, the use of flexible and adaptive strategies to respond to changing circumstances, and the use of leadership and decision-making techniques that are appropriate for the given situation.
In conclusion, there are various approaches to management that have been developed over the years, each with its own set of characteristics and principles. These approaches are based on different assumptions about human behavior, decision-making, and organizational structure, and they have been used by managers in different contexts and industries to achieve success. Understanding these approaches can help managers choose the most appropriate strategy for their organization and situation, and apply it effectively to achieve their goals and objectives.