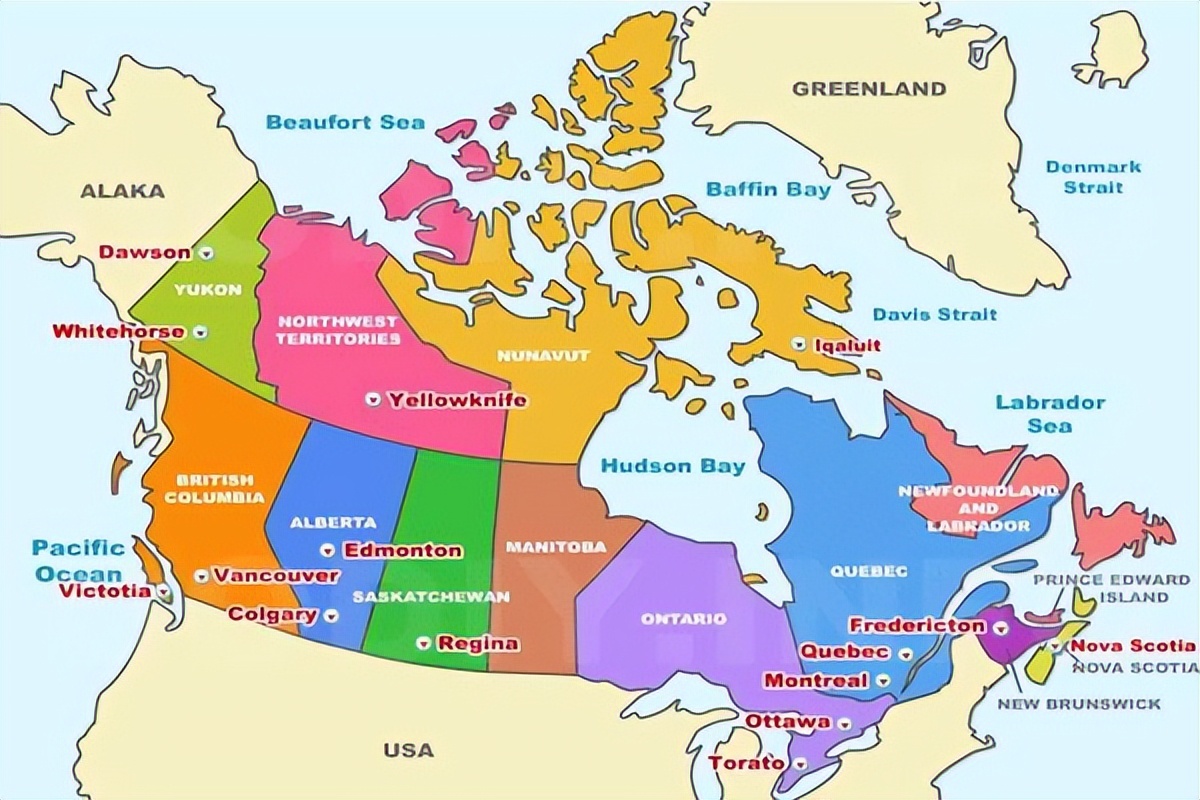
Canada is a country located in North America, bordered by the United States to the south and Alaska to the northwest. It is a sovereign nation with a rich history and a unique identity. Many people are curious about when Canada became independent, and the answer is somewhat complex.
Canada was first settled by Indigenous peoples thousands of years ago, and it was later explored and claimed by European powers, including France and Britain. In 1763, the Treaty of Paris was signed, which transferred the French colony of New France, which included much of what is now Canada, to Britain. For the next century and a half, Canada was a British colony, and its affairs were largely controlled by the British government.
However, Canada began to gain more autonomy and self-governance as it developed and matured. In 1867, the British North America Act was passed, which established the Dominion of Canada as a self-governing country within the British Empire. This marked a significant step towards independence for Canada, as it was given the power to govern itself and make its own laws, subject to the approval of the British Parliament.
Throughout the 20th century, Canada continued to gain more independence and autonomy from Britain. In 1982, the Constitution Act was passed, which patriated the Canadian Constitution from Britain and gave Canada full control over its own affairs. This act effectively made Canada an independent country, with the ability to make its own decisions and chart its own course without interference from Britain or any other foreign power.
In summary, Canada has a long and complex history, and it did not become fully independent overnight. It took many years and a series of important events and decisions to bring Canada to where it is today as a sovereign nation. However, it is clear that Canada has come a long way from its days as a British colony, and it is now a proud and independent country that is respected and recognized on the world stage.
History of Canada (1763

Lost Initiatives: Canada's Forest Industries, Forest Policy, and Forest Conservation. In my experience, it seems to be that the older someone is, the more likely they are to like the monarchy. Histoire populaire du Québec, Tome 1, des origines à 1791. A Liberal with 22 years in office, he was the longest-serving Prime Minister in Canadian history. Defence, Not Defiance: A History Of The Bermuda Volunteer Rifle Corps.
Canada's Long, Gradual Road to Independence

Yet the universal neglect of our colonial defences is apparent in the fact that no telegraphic communication has hitherto been established with the West Indies on the one side, or with the Dominion of Canada on the other. Retrieved July 28, 2021. Anyway this annoyed the separatist provinces further south who were so against the commercial consequences of these rights conferred by George III in 1763, that they complained about it in their Declaration of Independence a couple of years later. During the election campaign, King focussed on this constitutional issue, managing successfully to divert public attention from the Customs Scandal that originally gave rise to the problem and was a blot on his government's reputation. We recognize the resilience of Indigenous storytellers and Knowledge Keepers who have kept their stories alive despite attempts to silence them. We could have joined the separatists but we favoured negotiation, debate, protest, patience. English Canada started its life with as powerful a nostalgic shove backward into the past as the Conquest had given to French Canada: two little peoples officially devoted to counter-revolution, to lost causes, to the tawdry ideals of a society of men and masters, and not to the self-reliant freedom alongside of them.
Canada's Independence
Retrieved April 13, 2010. The Routledge Handbook of American Military and Diplomatic History: The Colonial Period to 1877. Retrieved April 16, 2010. Therefore the new confederation comprised of four provinces: Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec, and Ontario. Despite not liking the monarchy at all myself, I wouldn't describe the people who do like the monarchy as "whacko monarchists" as someone else put it, though some certainly exist.
When did Canada become a completely independent country?

The Founding of New Societies: Studies in the History of the United States, Latin America, South Africa, Canada, and Australia. It took five decades after the Statute of Westminster for Canada to make its final step toward full sovereignty. Retrieved October 2, 2009. Bothwell, Drummond and English state: That support was remarkably uniform geographically and racially, both coast to coast and among French and English. The Dominion Partnership in Imperial Defense, 1870—1914. It also suggests that contemporary allusions to sovereignty should be treated skeptically.






.svg/350px-Quebec_referendum%2C1995_-_Results_By_Riding_(Simple_Map).svg.png)