Price elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in its price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price. A good or service is said to be elastic if a small change in price results in a large change in quantity demanded, and inelastic if a large change in price is required to produce a significant change in quantity demanded.
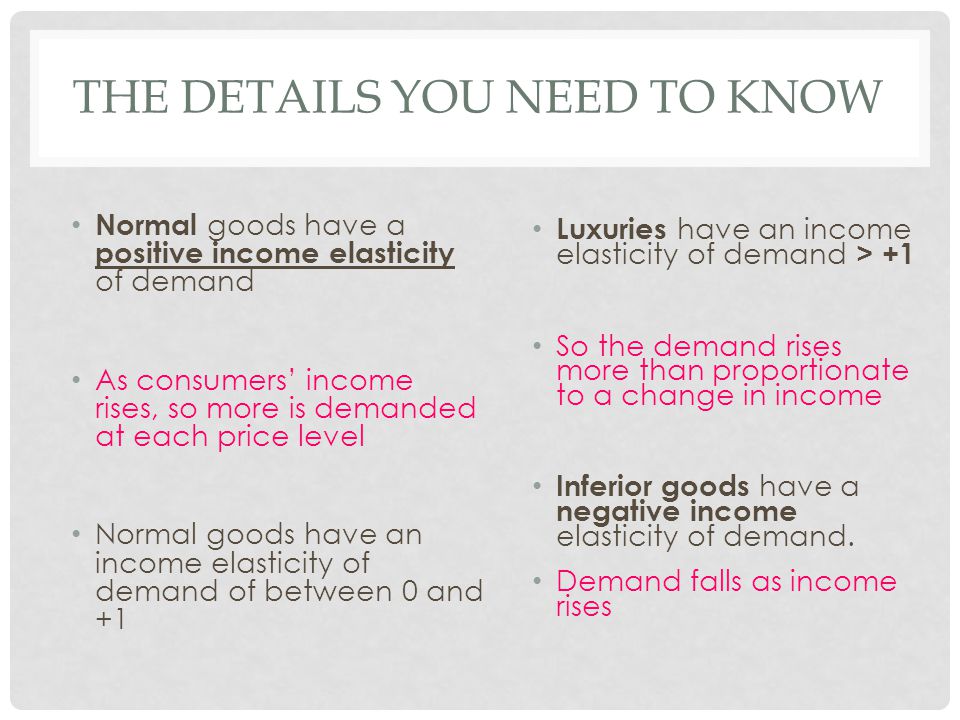
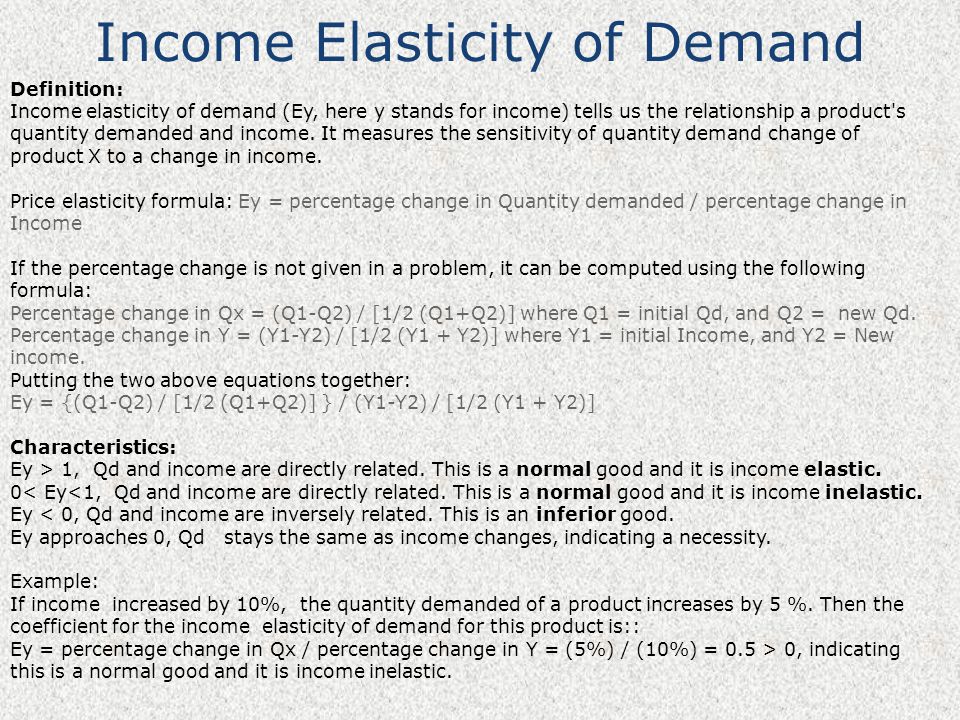
Income elasticity of demand is a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good or service to a change in the income of the consumer. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in income. A good or service is said to be income elastic if an increase in income leads to a proportionally larger increase in the quantity demanded, and income inelastic if the quantity demanded remains relatively unchanged despite an increase in income.
There are several factors that can influence the elasticity of demand for a particular good or service. These include the availability of substitutes, the necessity of the good or service, and the proportion of income that is spent on the good or service.
For example, a luxury item such as a designer handbag may be highly elastic, as consumers may be willing to reduce their demand for the item if the price increases significantly. On the other hand, a necessity such as food may be inelastic, as consumers will continue to purchase it despite changes in price.
Income elasticity of demand can also vary significantly among different goods and services. Normal goods, which are those that are consumed more when income increases, are likely to have a positive income elasticity of demand. Inferior goods, on the other hand, are those that are consumed less when income increases and are likely to have a negative income elasticity of demand.
In conclusion, price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price, while income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in income. Both measures are important in understanding consumer behavior and can be used to make informed decisions about pricing and marketing strategies.
Elasticity of Demand: Price, Income and Cross
It is defined as the responsiveness of demand to a change in price, while other things remain unchanged. ADVERTISEMENTS: Elasticity of demand is of three types — price, income and cross. In expansions, demand for all types of goods and services is higher and therefore businesses charge more. Demand for a normal good grows with an increase in customer wages and vice versa, assuming other factors of demand are constant. Stigler, Trends in Employment in the Service Industries Princeton, N.
Income Elasticity of Demand: Definition, Formula, and Types
Therefore, none of the goods can be inferior. Consumer discretionary products such as premium cars, boats, and jewelry represent luxury products that tend to be very sensitive to changes in consumer income. Hence if demand is elastic at all points on the demand curve, every reduction in price must increase total expenditure. Also, It can be positive or negative depends upon the type of goods demanded whether normal or inferior. Elasticity of Demand vs Price Elasticity of Demand Similar in meaning to the expansion of a rubber band, elasticity of demand refers to how changes in X which can be anything such as price, income, etc.
Income Elasticity, Price Elasticity, and Cross Elasticity

When the price of a good with a close substitute, say cauliflower, increases, the demand for that particular product will likely shift to another vegetable, say broccoli. It is the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage change in income of the consumer. Then they will react strongly to the price changes. Special Considerations: Understanding the Economy Income and prices are two variables followed by economists at large. The four main types of elasticity of demand are price elasticity of demand, cross elasticity of demand, income elasticity of demand, and advertising elasticity of demand. When an economy is expanding it usually comes with rising inflation due to increased demand.
Income Effect vs. Price Effect: What’s the Difference?

Conversely, complementary goods, like cell phones and chargers, have negative cross-price elasticity. The equations were fitted in both weighted 1958 state populations and unweighted form. ADVERTISEMENTS: The main determinants of income elasticity are: 1. A high value for e p implies that quantity is proportionately very responsive to price changes. Income elasticity of demand: Based on the calculation of the price elasticity coefficient of demand, products can be classified into the categories of inferior, luxury, normal, necessities, etc. Knowing this difference, you can distinguish between price elasticity and income elasticity of demand.
Difference between Price Elasticity and Income Elasticity

This form underlies the cardinal utility based demand theory of Alfred Marshall. His book, The Clash of Progress and Security, published in 1935, is perceptive and contains much that is relevant to the problems of Cohn Clark's writings on this point are better known, particularly his often- quoted conclusion, "We may well now turn to examine what much careful gen- eralization of available fact shows to be the most important concomitant of eco- nomic progress, namely, the movement of working population from agriculture to manufacture, and from manufacture to commerce and services. The results of this preliminary inquiry into a very complex econometric problem are consistent with the conclusions based on sector trends in output. Under Assumption II gross product in current dollars , real output in services rose 0 per cent per annum faster than in goods. The basic determinants of the elasticity of demand of a commodity with respect to its own price are: ADVERTISEMENTS: 1 The availability of substitutes; the demand for a commodity is more elastic if there are close substitutes for it.