Basic research and applied research are two types of research that are conducted for different purposes and have different characteristics.
Basic research, also known as pure or fundamental research, is research that is conducted for the purpose of increasing our understanding of fundamental principles or phenomena. It is curiosity-driven and seeks to answer questions about the underlying nature of things. Basic research is often theoretical and is not necessarily motivated by any practical or immediate application. It is often funded by universities, government agencies, and foundations and is usually conducted by academic researchers.
Examples of basic research include studies on the structure of the universe, the nature of light, and the genetic basis of diseases. Basic research can lead to new discoveries and theories that can be applied in the future, but it may not have any immediate practical implications.
On the other hand, applied research is research that is conducted with the specific purpose of solving practical problems or developing new technologies or products. It is problem-driven and aims to find solutions to specific problems or to improve existing technologies or processes. Applied research is often conducted by government agencies, businesses, and other organizations that are interested in finding practical solutions to real-world problems.
Examples of applied research include studies on the development of new medical treatments, the design of new products or technologies, and the improvement of existing production processes. Applied research is often more focused and specific than basic research, and it is usually conducted with a specific end goal in mind.
In summary, basic research is research that is conducted to increase our understanding of fundamental principles, while applied research is research that is conducted to solve practical problems or develop new technologies or products. Both types of research are important and have their own unique characteristics and goals.
Basic vs. Applied Research: Definitions and Examples

Basic research looks at how processes or concepts work. This research type uses empirical methodologies, such as experiments, to collect further data in an area of study. Nature Basic research is more theoretical since it generally generates theories and explores information which may not be presently applied. Basically, we showed that if locations are mentioned together, they are located together. The nature-nurture issue centers on the relative contributions of genes and experience, and their interaction in specific environments.
Exam 1 Flashcards
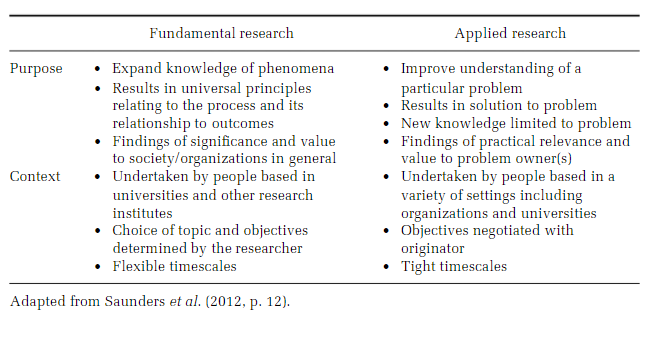
Hence, fundamental research is purely theoretical as it delves into basic laws and principles. To gain future insights and information from various already existing sources, researchers adopt the Basic research methodology. Typically, you conduct this kind of research when you're hoping to expand existing knowledge and create predictions. Researchers sometimes use these methods interchangeably for both types of research. Generally, applied research deals with particular topics which have direct practical relevance. Now, estimating the geographical location based on the way it is mentioned in language is basic research par excellence. An Overview on the Difference between Basic and Applied Research Guide 2022 There are several research options in the realm of science, and all research contains comparable aspects regardless of the subject or breadth it addresses.
11 Honest Difference between Basic and Applied Research
.png)
Strategy It plans the strategy. Once you grasp it, the research method will be less complicated than ever Frequently Asked Questions on Basic vs Applied Research What is the key difference between basic vs applied research? Our autonomic nervous system ANS controls our glands and our internal organ muscles. A short brief on basic and applied research The approach of basic research is solely based on theories. Often, governments and industries favor applied research over basic research. Basic research is executed without thought of a practical end goal, without specific applications or products in mind. Instead, it largely comes down to your personal preferences and the type of researcher you are. However, in terms of applied research, it cannot discover new knowledge.






.png)
